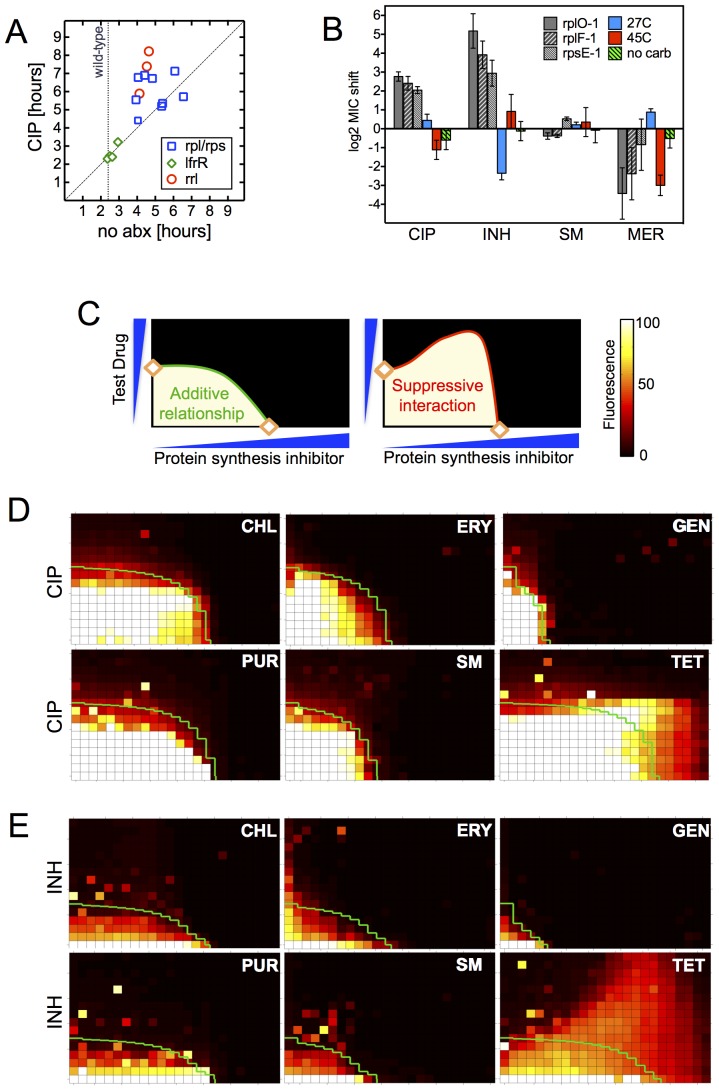
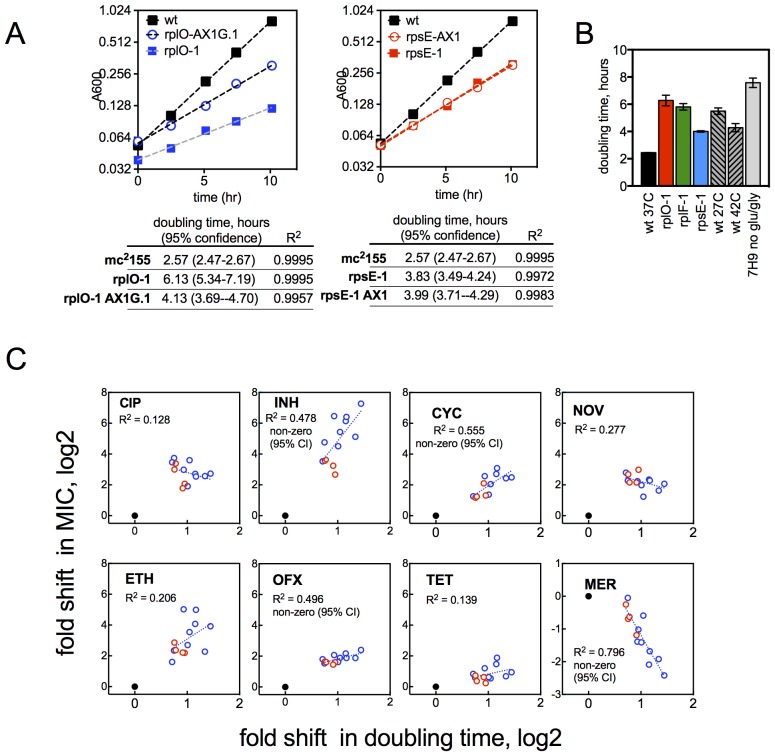
Figure 3. Resistance is not a simple consequence of slowed growth or general inhibition of translation.
(A) Doubling times in antibiotic-free medium (x-axis) or 0.3 μg/ml CIP (y-axis), each dot represents an individual mutant. (B). Shifts in antibiotic sensitivity upon altering growth rate of wild type bacteria by temperature or carbon availability (dextrose/glucose-free medium). Error bars = 95% confidence intervals. See Figure 3—figure supplement 1C for growth rates. (C) Checkerboard assay description: 384-well plates contain increasing concentrations of protein synthesis inhibitors along the x-axis and a second test antibiotic on the y-axis. Growth of M. smegmatis mc2155 (pUV3583cGFP) is measured by fluorescence. If the antibiotics are non-interacting then growth would follow the additive isobole in green (top box, see Supplementary Materials and methods). Antagonistic interactions extend growth beyond the isobole (bottom box). (D) Interaction of protein synthesis inhibitors chloramphenicol (CHL), erythromycin (ERY), gentamycin (GEN), puromycin (PUR) and streptomycin (SM) with CIP. (E) Same as (D) using INH. Tetracycline is unique in demonstrating antagonistic interactions with CIP and INH, phenocopying the ribosomal mutations.