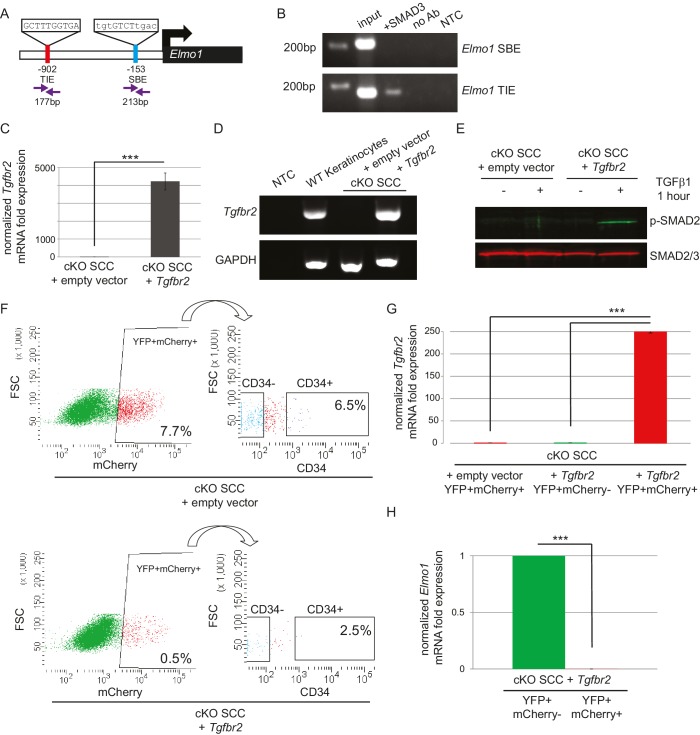
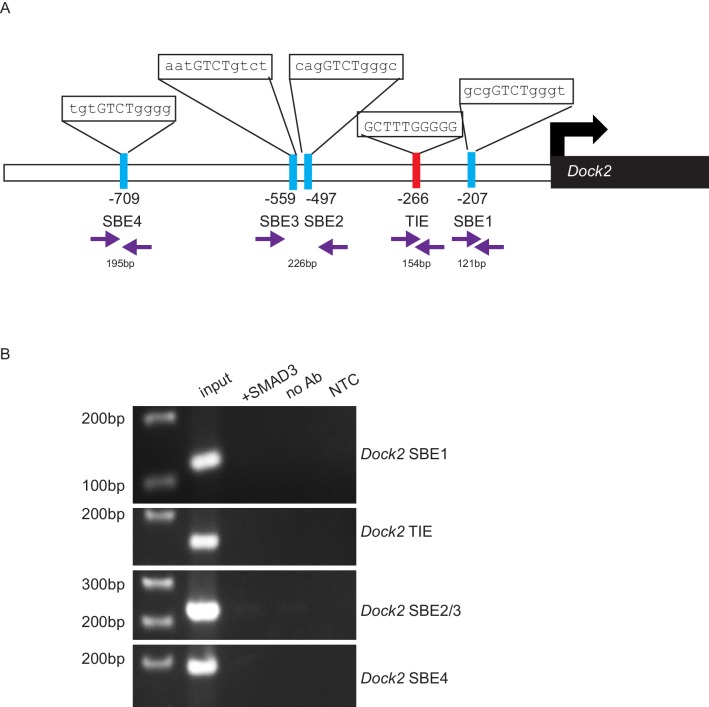
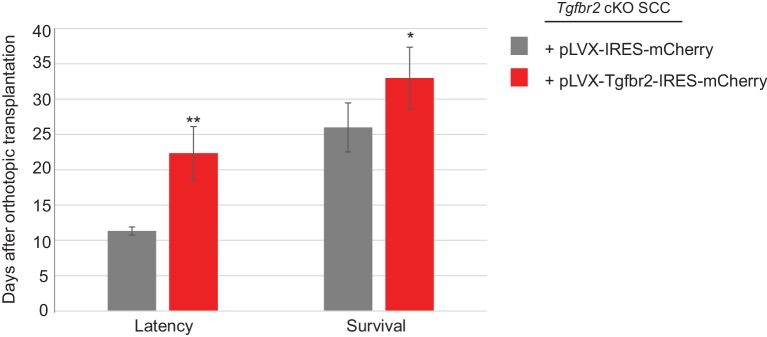
Figure 6. The GEF ELMO1 is a novel target of TGFβ signaling via SMAD3.
(A) Promoter analysis using MatInspector (Genomatrix) revealed two putative SMAD-responsive elements in the Elmo1 promoter. The consensus SMAD-binding element (SBE) sequence GTCT was identified 153 base pairs (bp) upstream of the Elmo1 transcriptional start site, and the consensus TGFβ-inhibitory site (TIE) GNNTTGGNGN was identified 902 bp upstream of the Elmo1 transcriptional start site. Primers were designed to flank these sites (purple arrows). (B) Chromatin immunoprecipitation with an anti-SMAD3 antibody was used to isolate DNA fragments that were amplified by the primers designed to flank the Elmo1 TIE, but not the Elmo1 SBE, after overexpressing SMAD3 in NIH3T3 cells and treating with TGFβ1 (2 ng/ml) for 24 hr. Non-template (NTC) and no-antibody (no Ab) controls were used to verify the specificity of binding. (C–E) Lentiviral infection of Tgfbr2 cKO CD34+ SCC cells with the full-length Tgfbr2 gene inserted into the pLVX-IRES-mCherry vector resulted in rescue of Tgfbr2 mRNA by more than 4000-fold (C–D) and phosphorylated SMAD2 (p-SMAD2) in response to treatment with TGFβ1 (2 ng/ml) for 1 hr (E), compared to Tgfbr2 cKO CD34+ SCC cells infected with the empty pLVX-IRES-mCherry vector. No Tgfbr2 mRNA was detected in Tgfbr2 cKO CD34+ SCC cells infected with the empty pLVX-IRES-mCherry vector. Data represent the mean ± standard deviation; student’s t-test, ***p=0.000112. (F–I) Tumors generated from orthotopic transplantation of 100,000 Tgfbr2 cKO CD34+ SCC cells infected with empty vector or with full-length Tgfbr2 were dissociated and YFP+mCherry+, YFP+mCherry-CD34+ and YFP+mCherry-CD34− cells were isolated by FACS and subjected to RNA extraction. (F) Approximately 7.7% of the cKO SCC + empty vector total tumor bulk expressed mCherry, whereas 0.5% of the cKO SCC + Tgfbr2 expressed mCherry at the time of analysis. See also Figure 6—figure supplement 2. The frequency of YFP+mCherry+CD34+ cells was significantly reduced in the rescued cKO SCC + Tgfbr2 tumor. (G) YFP+mCherry+ cells isolated from tumors generated from Tgfbr2 cKO CD34+ SCC cells infected with full-length Tgfbr2 expressed Tgfbr2 mRNA 250-fold over YFP+mCherry- cells isolated from the same tumor or YFP+mCherry+ cells isolated from tumors generated from Tgfbr2 cKO CD34+ SCC cells infected with empty vector (***p=0.000005). No Tgfbr2 mRNA was detected by qRT-PCR in YFP+mCherry- cells isolated from tumors generated from Tgfbr2 cKO CD34+ SCC cells infected with full-length Tgfbr2 or YFP+mCherry+ cells isolated from tumors generated from Tgfbr2 cKO CD34+ SCC cells infected with empty vector. (H) Rescue of TGFβRII abolished Elmo1 mRNA expression in YFP+mCherry+ cells isolated from tumors generated from Tgfbr2 cKO CD34+ SCC cells infected with full-length Tgfbr2 compared to YFP+mCherry-CD34+ cells isolated from the same tumor. Data represent the mean ± standard deviation. Asterisks denote statistical significance using two-tailed, unpaired student’s t-test; p***=9×10−24. Three different tumors for each condition have been analyzed.