Fig. 2.
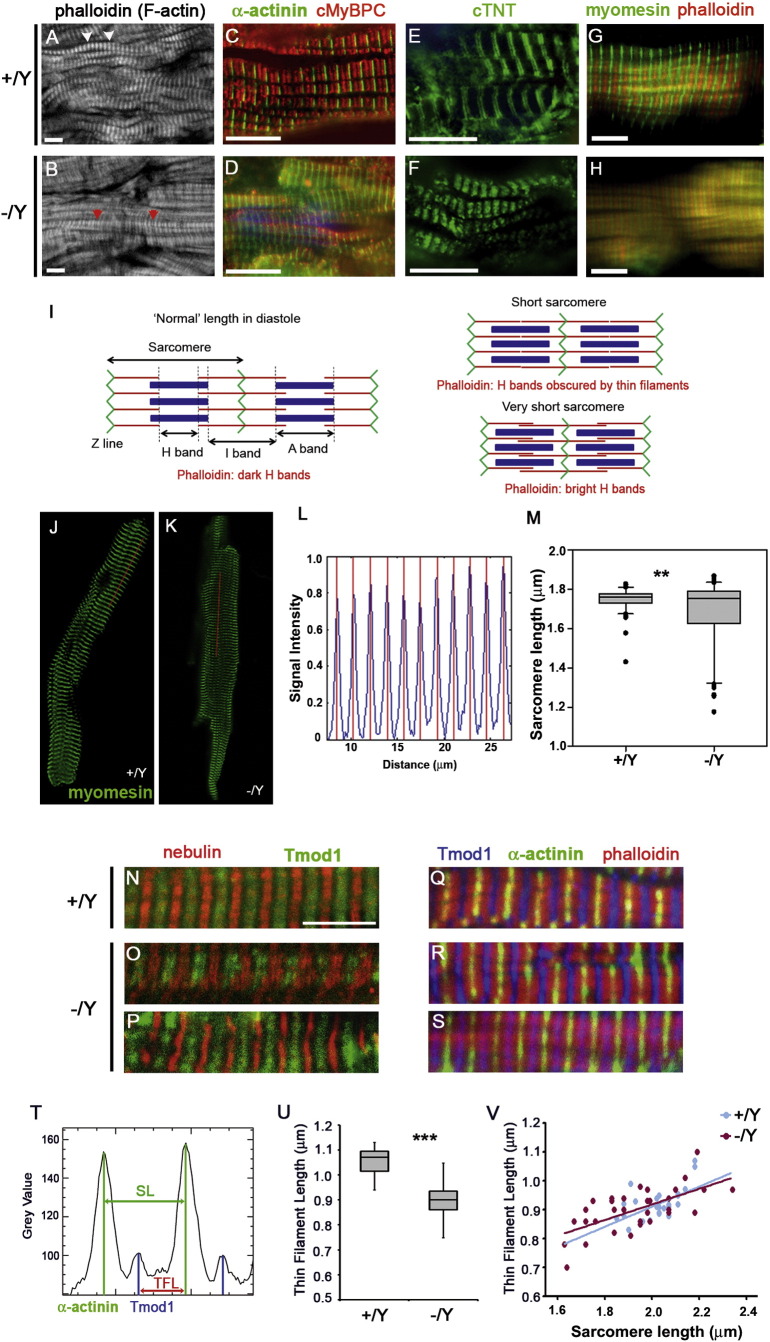
Dysregulated sarcomere length in Tβ4 −/Y myocardium. Assessment of sarcomeric components in diastole-fixed adult heart sections (n = 5 per genotype): filamentous actin (A, B), α-actinin/cMyBPC (C, D), cardiac troponin T (cTNT; E, F), myomesin/phalloidin (G, H). Staining of polymerized actin with phalloidin revealed that > 60% of −/Y cardiomyocytes contained shortened sarcomeres (B), compared with +/Y (A). Schematic in I illustrates how short sarcomeres in −/Y hearts present with additional phalloidin bright bands (red arrowheads in B) compared with normal diastolic sarcomeres in +/Y hearts (white arrowheads in A), in which clear dark bands are seen either side of the Z line. Shorter sarcomere length was also evident upon visualisation of Z-disc, thick filament proteins (α-actinin, D, compared with C; cMyBPC, D, compared with C; myomesin, H, compared with G), and components of the troponin complex (cTNT, F, compared with E) and M band (H, compared with G). Representative images of cardiomyocytes from +/Y (J, n = 55) and −/Y (K, n = 63) mice. Sarcomere length was assessed by finding peaks within a plot of image intensity (L) over a line perpendicular to striations (J, K) and revealed a negative skew in its distribution. Mean sarcomere length was determined for each cell and the population of means illustrated via box-and-whisker (M). Means (1.75 μm +/Y, 1.68 μm −/Y) were significantly different by 1-way ANOVA (p < 0.01). Thin filament length (TFL) was assessed by examining nebulin/Tmod1 banding (N—P) and measured as distance between the peaks, in intensity profile, of Tmod1 and α-actinin (Q–T). In keeping with shortened sarcomere length in −/Y hearts, TFL was found to be more variable and, overall, significantly shorter in −/Y hearts (U; 0.98 ± 0.09 μm vs. 1.06 ± 0.05 μm in +/Y hearts; p < 0.001 by 1-way ANOVA). TFL correlates with SL in both +/Y and −/Y hearts (V). By linear regression analysis, both slopes were significantly different from zero (+/Y: 0.0006 and −/Y: < 0.0001) but were not significantly different between genotypes, in terms of slope, elevation or intercept. Scale bars: A–H: 10 μm; N (applies to N–S: 5 μm). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)