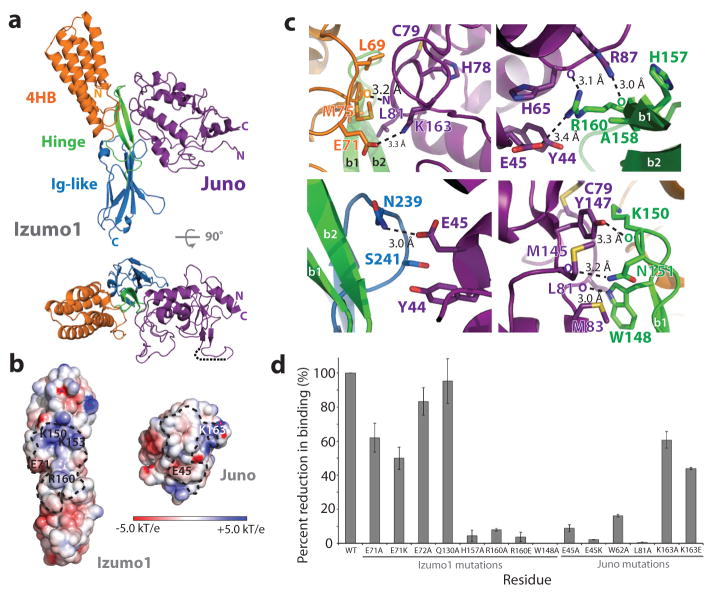
Figure 2. Izumo1-Juno heterotypic assembly.
(a) Crystal structure of the human Izumo122-254-Juno20-228 complex shown as a ribbon diagram. Izumo122-254 and Juno20-228 are coloured according to Figure 1. A disordered loop between the β1 and β2 strands of the Juno20-228 is shown with a black dashed line. (b) Electrostatic potential surface representation of the Izumo122-254-Juno20-228 binding interface. The footprints of the binding interface are shown by black dashed lines. R160 and E71 on Izumo1 form a salt bridge with E45 and K163 on Juno, respectively. (c) Binding site interactions of Izumo122-254 and Juno20-228. Side chains of key residues involved in hydrogen bond or salt bridge interactions are shown. (d) BLI binding affinity analysis of Izumo122-254 and Juno20-228 interface mutants. Wild-type Izumo1-Juno interaction is normalized at 100% and the binding affinities (Kd) for each mutant is shown as a percent reduction to wild-type. All experiments were performed with technical triplicates (n=3), with mean Kd values and its standard deviations of the mean presented in Extended Data Table 1.