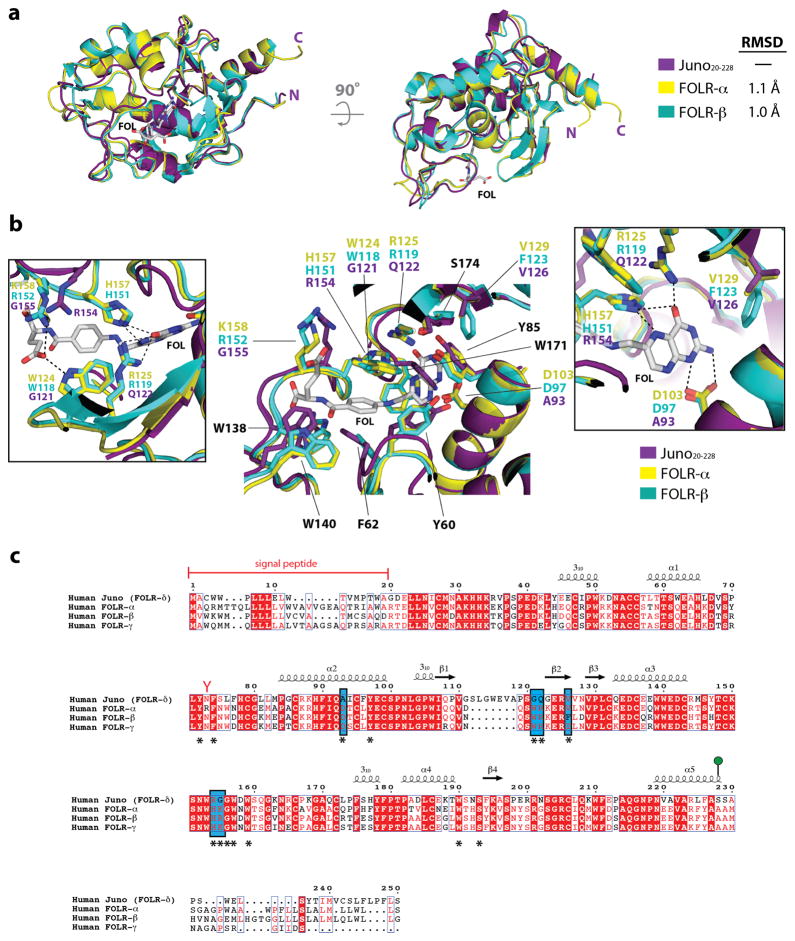
Extended Data Figure 4. Structural comparison of Juno and the folate receptor family of proteins.
(a) Structural superimposition of Juno20-228 with FOLR-α (PDB ID: 4LRH) and FOLR-β (PDB ID: 4KMZ). Experimentally bound folate (FOL), shown in white sticks, from the FOLR-α structure is positioned in the active site. (b) Superimposition of residues in the folate-binding site of human FOLR-α and FOLR-β, and equivalent residues in human Juno. Residue names shown in black are conserved between Juno, FOLR-α, and FOLR-β, and are numbered based on the FOLR-α sequence. Inset boxes highlight the residue differences between Juno, FOLR-α, and FOLR-β. Key hydrogen bond interactions are shown as dashed black lines. Mutagenesis studies showed that replacement of D103/D97, which forms strong interactions to the N1 and N2 nitrogen atoms of the pterin moiety, results in decreased affinity by more than one order of magnitude15. Six folate-binding residues observed in FOLR-α, and FOLR-β (FOLR-α/FOLR-β: D103/D97, W124/W118, R125/R119, V129/F123, H157/H151, and K158/R152) are not conserved in Juno. Four of these residues (FOLR-α/FOLR-β: D103/D97, W124/W118, R125/R119, and H157/H151) form key hydrogen bonds to anchor folate in the active site. In Juno, the substituted residues are not able to maintain the extensive hydrogen bond network seen in FOLR-α and FOLR-β to folate. (c) Homo sapiens FOLR-α (Uniprot: P15328), FOLR-β (Uniprot: P14207), FOLR-γ (Uniprot: P41439) and FOLR-δ (Uniprot: A6ND01) are aligned. Red boxes indicate complete conservation of a given amino acid. N-linked glycosylation sequons (N-x-S/T) are indicated by red-coloured Y-shaped symbols. Juno is anchored to the plasma membrane through a GPI anchor at Ser228 (shown as a green lollipop). Experimentally determined secondary structural elements are shown as arrows for β-strands and coils for α-helices. Key folate-binding residues, identified from the FOLR-α and FOLR-β crystal structures, are identified with an asterisk underneath the sequence. Key residues difference between Juno, FOLR-α and FOLR-β folate binding sites are highlighted in a blue box.