Fig. 4.
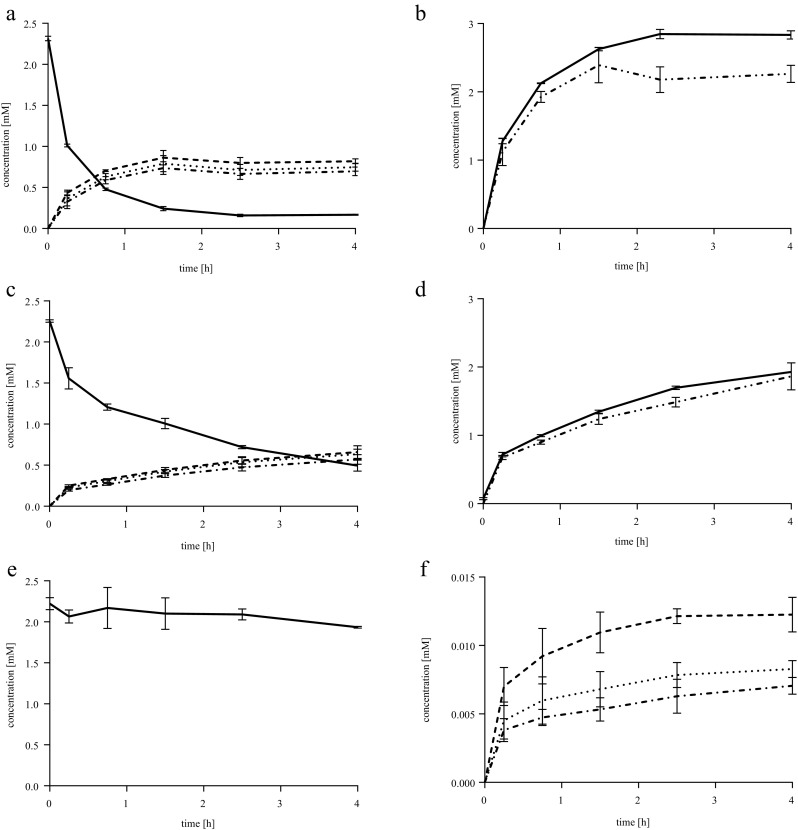
Conversions of lauric acid by different P450BM3 systems. All reactions contained 2.25 mM lauric acid, 4.0 mM phosphite, and 50 μM NADPH, thus making any product formation above 0.05 mM dependent on phosphite oxidation. a, b PTDH-P450BM3. c, d PTDH + P450BM3. e, f P450BM3. Samples were taken and analyzed by GC-MS to determine substrate depletion (a, c, and e; solid line) and product formation (a, c, and f) (9-hydroxylauric acid, dotted line; 10-hydroxylauric acid, dotted dashed line; 11-hydroxylauric acid, dashed line). In b and d, uncoupling was examined by following phosphate production measured with the molybdate assay (solid lines) and comparing it to total product formation determined by GC-MS (double dotted dashed line). For P450BM3 conversions, only a background of phosphate was detected (data not shown). All samples were measured in triplicate. Controls were reaction mixtures without enzyme and reaction mixtures without NADPH
