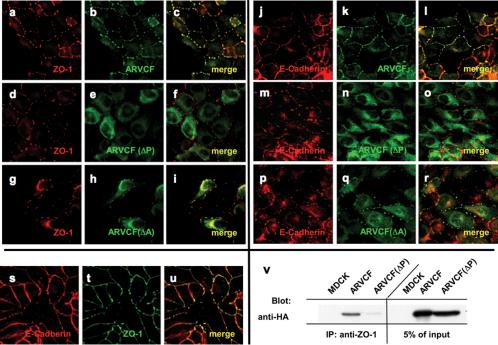
Figure 5.
Colocalization and coprecipitation of ARVCF and ZO-1 or E-cadherin in transfected MDCK cells treated with cytochalasin D. (a-u) Colocalization of ZO-1, E-cadherin, and ARVCF. MDCK cells transfected with wild-type ARVCF (a-c and j-l) or mutant ARVCF(ΔP) (d-f and m-o) or ARVCF(ΔA) (g-i or p-r) were fixed, permeabilized, and stained for ZO-1 (red, a, d, and g), E-cadherin (red, j, m, and p), and wild-type or mutant ARVCF (green, b, e, h, k, n, and q). Confocal images of the ZO-1 or E-cadherin and ARVCF labeling were merged to show regions of colocalization (yellow, c, f, i, l, o, and r). Colocalization of E-cadherin (red, s) and ZO-1 (green, t) in cytochalasin-treated cells is shown in yellow (u). v, ARVCF coprecipitates with ZO-1 from cytochalasin D-treated MDCK cells. Control cells (MDCK) or cells expressing ARVCF or ARVCF(ΔP) were lysed, and equal amounts of total protein were used to immunoprecipitate ZO-1. Precipitates were blotted to detect ARVCF that was bound to ZO-1. An aliquot of the cell lysate (5%) was directly blotted to determine the amount of wild-type and mutant ARVCF present in the lysates. Untransfected cells served as a control for the specificity of the precipitation.