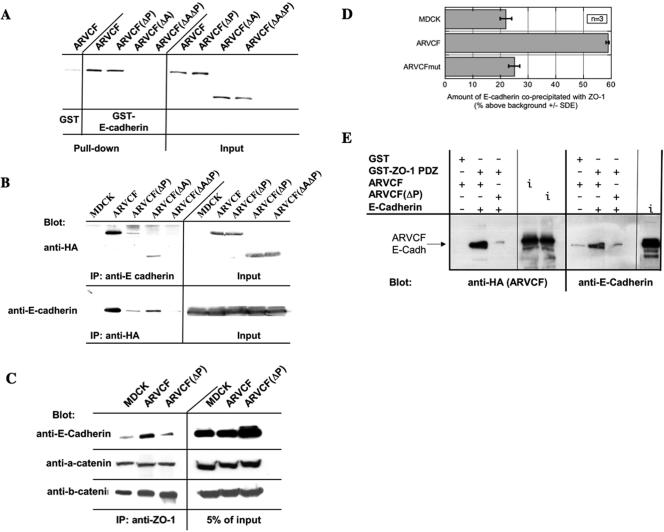
Figure 6.
Binding of ARVCF and E-cadherin. (A) Binding of in vitro-translated wild-type and mutant ARVCF to a GST fusion protein containing the cytosolic domain of E-cadherin. GST or GST-E-cadherin tail fusion proteins were coupled to glutathione beads and incubated with in vitro translated, radioactively labeled, ARVCF, ARVCF(ΔP), ARVCF(ΔA), or ARVCF(ΔAΔP). Protein bound to the beads (pull-down) was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. An aliquot (5%) of the in vitro-translated material was directly analyzed to confirm that similar amounts of the in vitro translated proteins were added to the binding reaction. (B) Coprecipitation of wild-type or mutant ARVCF with E-cadherin. Control cells (MDCK) or cells expressing ARVCF, ARVCF(ΔP), ARVCF(ΔA), or ARVCF(ΔAΔP) were lysed, and equal amounts of total protein were used to immunoprecipitate E-cadherin. Precipitates were blotted to detect ARVCF (anti-HA) that was bound to E-cadherin. Alternatively, wild-type or mutant ARVCF was precipitated with the anti-HA antibody, and precipitates were blotted to detect bound E-cadherin. An aliquot of the cell lysate (5%) was directly blotted to determine the total amount of ARVCF or E-cadherin, respectively, present in the lysates. Untransfected cells served as a control for the specificity of the precipitations. (C) Coprecipitation of ZO-1 and E-cadherin. Control cells (MDCK) or cells expressing ARVCF or ARVCF(ΔP) were lysed, and equal amounts of total protein were used to immunoprecipitate ZO-1. Precipitates were then analyzed by Western blot to detect E-cadherin that was bound to ZO-1. An aliquot of the cell lysate (5%) was directly blotted to determine the amount of E-cadherin present in the lysate. (D) Quantification. The relative amounts of E-cadherin that coprecipitated with ZO-1 from control cells or those expressing wild-type or mutant ARVCF was quantified. (E) In vitro association of ZO-PDZ, ARVCF, and E-cadherin. Immoblized GST or GST-ZO-1 PDZ domain fusion proteins were incubated with in vitro translated ARVCF or ARVCF(ΔP) and E-cadherin. Proteins bound to the beads were then identified by Western blot. An aliquot of the in vitro translation reaction was directly blotted (i; input) to monitor the amount of ARVCF, ARVCF(ΔP), and E-cadherin added to the reaction.