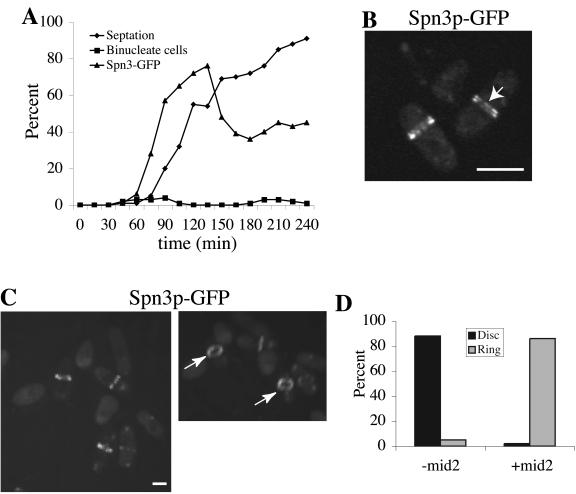
Figure 8.
Coalescence of septin rings can be induced during interphase by mid2+ expression. (A) spn3-GFP cdc16-116 (KGY738) cells were transformed with pREP41-HA-mid2+. Transformants obtained in the presence of thiamine in the medium were then grown to midlog phase in the absence of thiamine at 25°C for 15 h. They were then synchronized in early G2 phase by centrifugal elutriation and immediately shifted to 36°C. Samples of cells were collected every 15 min. One portion of each sample was imaged immediately to determine the percentage of septated cells and the percentage of cells with Spn3p-GFP medial localization. Another portion was fixed with ethanol and stained with DAPI to determine the percentage of binucleate cells. (B and C) Spn3p-GFP localization in live cells at the 75-min time point. In B, cells imaged with a single Z-series stack (0.49 μm) are shown to provide the best visualization of split septin rings as indicated by the arrow. In C, the image in the left panel represents a 3D reconstruction of Z-series stacks. This image was rotated in the Z-axis (right panel) to illustrate the cortical restriction of the septin rings. The arrows point to organized septin rings. (C) Quantitation of disorganized septin rings (disk) and organized septin rings (ring) in interphase cdc16-116 cells in the presence or absence of Mid2p. Percentages were determined by visual inspection of Z-series stacks of live cells that contained medially placed septin structures from the experiment described in Figure 7A, 75-min time point, 93 cells examined (-mid2) and from the experiment described in part A of this figure, 75-min time point, 88 cells examined (+mid2). Scale bar, 5 μm.