Figure 8. Hypothetical mechanism for palmitic acid-induced autophagy and apoptosis in podocytes.
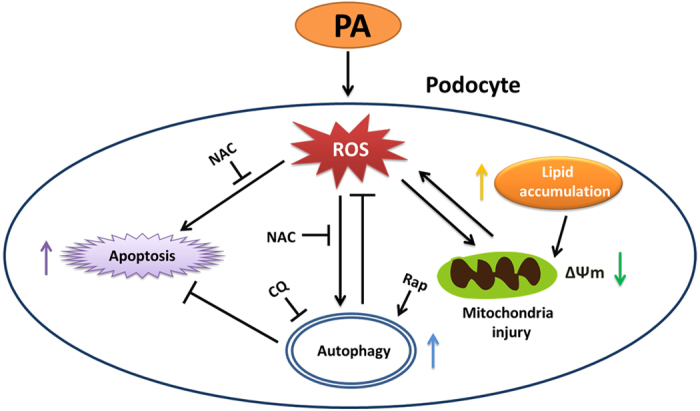
PA exposure induces an abnormal accumulation of lipids, which may induce mitochondrial injury. Mitochondria are both the major source of intracellular ROS production and targets of ROS, and mitochondrial damage can lead to excessive ROS generation, which can induce autophagy and apoptosis. On the other hand, autophagy serves as a protective mechanism through an unknown pathway, reducing excessive ROS production and protecting against palmitic acid-induced apoptosis in podocytes.
