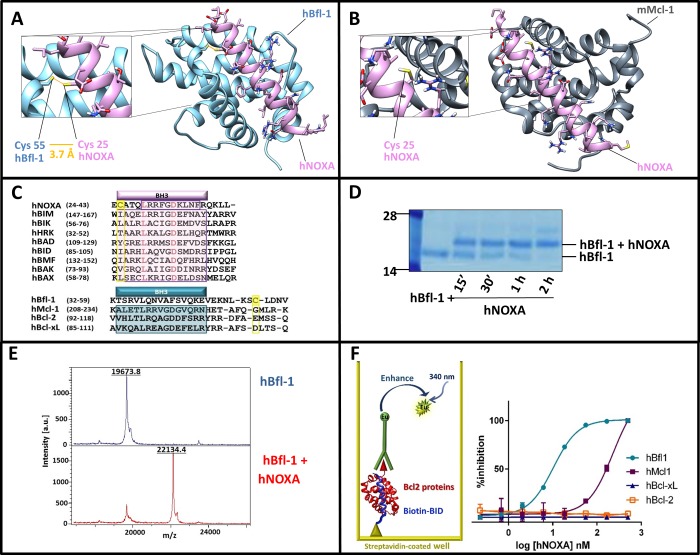
Figure 1.
Human NOXA interacted with human Bfl-1 covalently and potently, and with higher affinity compared to human Mcl-1. Panel A: Structure of hBfl-1 and hNOXA complex with a close-up view of the covalent bond between the Cys 55 of hBfl-1 and the N-terminal Cys of a hNOXA derived peptide (see sequence in Table 1) modeled on the hNOXA BH3 peptide cocrystallized with hBfl-1 (PDB ID: 3MQP). The newly formed bond is colored in orange, while hBfl-1 is represented by light blue ribbons and hNOXA peptide by pink sticks and ribbons. Panel B: Binding pose of a hNOXA derived peptide modeled on the hNOXA BH3 peptide cocrystallized with mMcl-1 (PDB ID: 2JM6)2. The close-up view shows the absence of a covalent interacting Cys residue in the BH3 hydrophobic cleft of mMcl-1, here represented by gray ribbons while hNOXA peptide by pink sticks and ribbons. Panel C: Sequence alignment of selected pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins hBIK, hHRK, hBIM, hBAD, hBID, hBMF, hNOXA, and the hBAX subfamily proteins hBAX and hBAK (upper panel). Structural alignment (lower panel) of selected antiapoptotic Bcl-2 proteins hBfl-1, hMcl-1, hBcl-2, and hBcl-xL. Bcl-2 Homology (BH) regions belonging to pro-apoptotic and antiapoptotic proteins are included in pink and blue rectangular boxes, respectively. Interacting Cys residues present in both hBfl-1 (Cys 55) and hNOXA (Cys 25) are highlighted in yellow, while red-colored residues indicate strictly conserved residues of pro-apoptotic proteins. Panel D: SDS-PAGE gel electrophoresis followed by Coomassie staining of the hBfl-1 protein (10 μM) in the absence and presence of equimolar concentrations of a hNOXA derived peptide (Table 1) at different time points (15 min, 30 min, 1h, 2h). Panel E: MALDI-TOF MS spectra of hBfl-1 collected in absence (blue) and presence (pink) of a hNOXA derived peptide (Table 1) after 2 h incubation at RT and at a protein–ligand ratio of 1:2. Panel F: Cartoon representing the principle of the DELFIA assays. These assays were used to quantify the ability of our test peptides to displace a biotinylated BID BH3 peptide from hBfl-1, hMcl-1, hBcl-xL, and hBcl-2. Representative DELFIA dose–response curves relative to the hNOXA derived peptide (Table 1) against these proteins are reported.