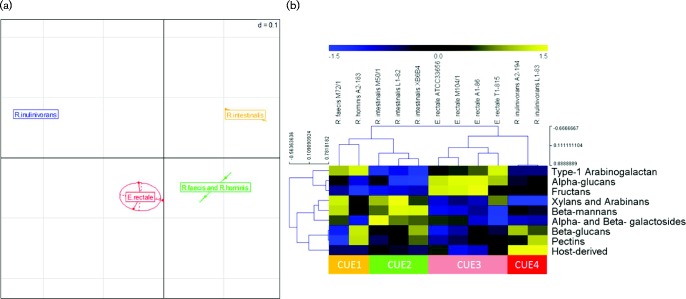
Fig. 3.
(a) Principal coordinate analysis of Roseburia/E. rectale strains based on complement of GH families and (b) heatmap showing CUEs. Values of a given GH family or carbohydrate set were taken as the number of these genes each genome possessed. In (a), coordinates were calculated using Kendal τ distance applied to the first five eigenvectors. R. intestinalis strains L1-82, M50/1 and XB6B4 (orange); R. inulinivorans strains A2-194 and L1-83 (blue); R. faecis M72/1 and R. hominis A2-183 (green); and E. rectale strains A1-86, T1-815, M104/1 and ATCC33656 (red) form separate clusters (P < 0.001, non-parametric multivariate ANOVA). In (b), CUEs were determined by complete linkage clustering using Kendall τ (as shown) and Spearman distance (not shown). GH53, an endo-1,4-β-galactanase that cleaves the β-1,4-d-galactosidic linkages in type I arabinogalactans, was assigned to the carbohydrate set ‘Type 1 arabinogalactan’ and is excluded from ‘Xylans and Arabinans’, ‘Pectins’ and ‘Alpha- and Beta-galactosides’. CUE1 consists of R. faecis M72/1 and R. hominis A2-183. CUE2 consists of R. intestinalis strains L1-82, M50/1 and XB6B4. CUE3 consists of E. rectale strains A1-86, T1-815, M104/1 and ATCC33656. CUE4 consists of R. inulinivorans strains A2-194 and L1-83. GH assignment to each carbohydrate set is described in Table S6.