Figure 1.
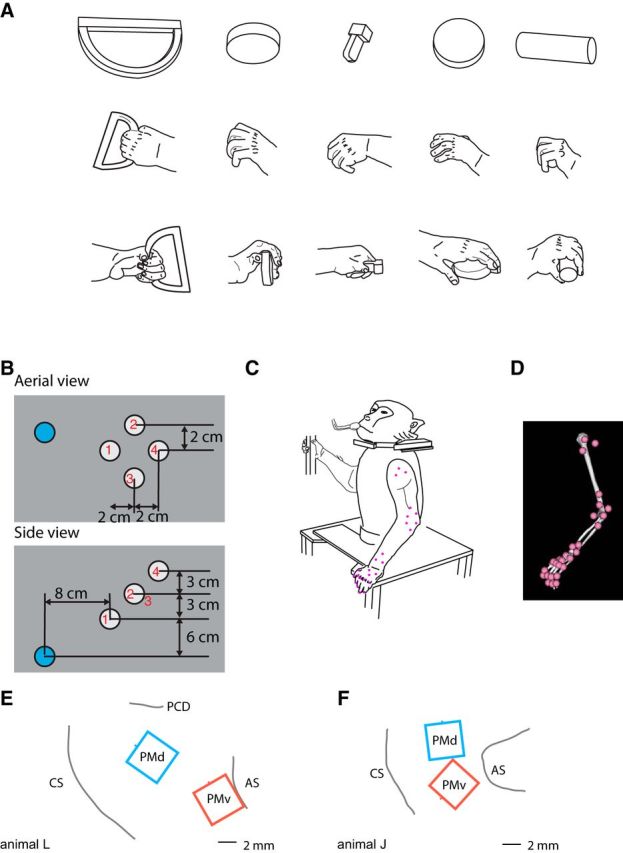
Methods. A, Animals were trained to grasp a variety of geometric shapes including (left to right) ring (vertical), small disc (out), key, small disc (horizontal), and cylinder (horizontal). These drawings depict static hand conformation during grasping of these objects. B, Target locations in relation to the starting position. Aerial view is shown at the top and side view at the bottom. Blue circle denotes the starting position and white circles denote target locations. Red numbers in or near the target circles indicate the location numbers 1–4. C, Drawing of animal J in rest position. Pink dots correspond to the approximate placement of the infrared markers. D, Depiction of the arm in the same position as in C in the Opensim software environment. E, F, Placement of electrode arrays in animals L and J, respectively. CS, Central sulcus; AS, Arcuate sulcus; PCD, Precentral dimple.
