Figure 7.
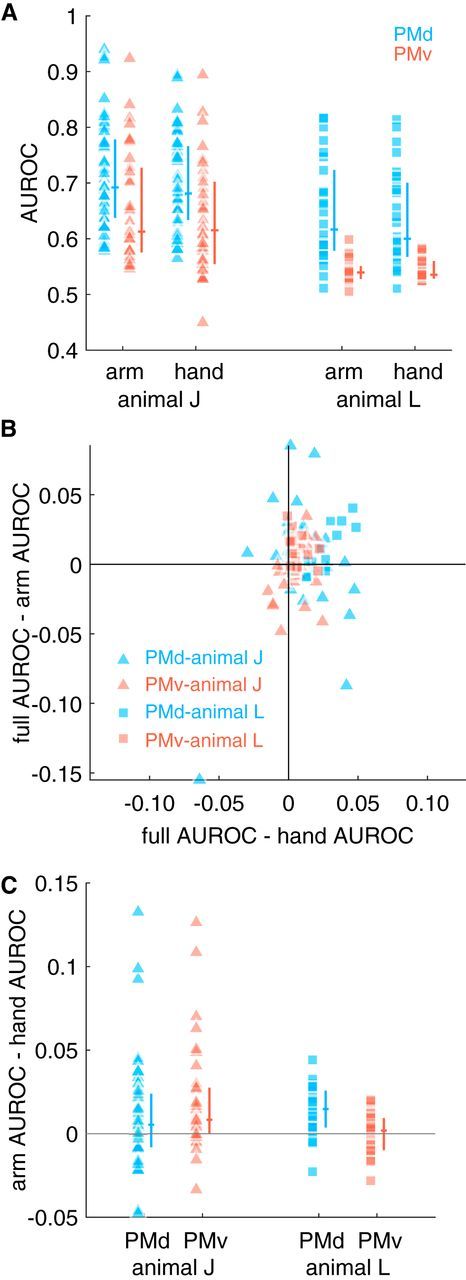
Comparing encoding performance of models based on an anatomical division of the upper limb. A, We fit GLMs using either arm or hand (including wrist) kinematics. For each model type and animal, the distribution of median AUROCs across folds is shown as raw data (left column; each point corresponds to a cell) and interquartile range + median (vertical and horizontal lines, respectively). B, Median AUROCs were compared between the full model that included all kinematic terms and reduced models that contained only arm or only hand kinematics. C, Distribution of differences in arm and hand AUROCs. We found that arm kinematics were encoded preferentially by PMd in both animals and also in PMv in animal J because a significant proportion of cells preferred arm kinematics in those two areas (significance codes: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005; see main text for additional statistics).
