Figure 1.
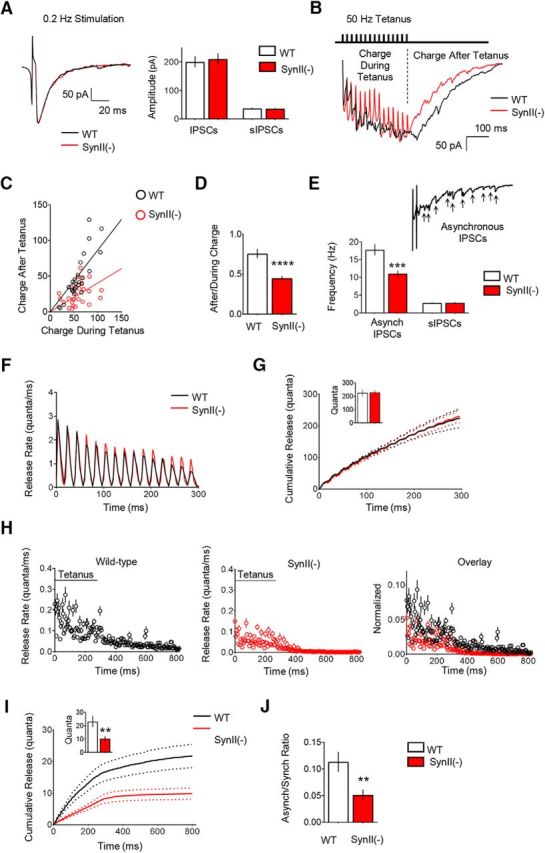
The asynchronous release component is reduced at SynII(−) inhibitory hippocampal synapses. A, Basal inhibitory transmission is similar at WT and SynII(−) slices. The stimulation intensity was adjusted to eliminate transmission failures, and this stimulation paradigm produced similar IPSC amplitudes in WT in SynII(−) lines. B, Representative postsynaptic currents elicited by 50 Hz frequency tetani at WT and SynII(−) slices illustrate the reduced after tetanus current in SynII(−) line (red). Stimulus artifacts were removed for clarity. C, The relationship between the charge transfer after a tetanus and the charge during a tetanus at individual experiments. The slope of the linear regression is significantly reduced at SynII(−) slices (p < 0.01), suggesting a selective reduction of the charge transfer after the tetanus in the Syn II(−) line. D, The After/During charge ratio is significantly reduced at SynII(−) slices (p < 0.001). E, The frequency of asynchronous current peaks is significantly reduced at SynII(−) slices (p < 0.005), whereas the sIPSC frequency is not affected. sIPSCs were collected for 5 min before the onset of the stimulation. F, The synchronous release component at WT and SynII(−) slices over the duration of the tetanus computed using deconvolution. G, The cumulative synchronous release kinetics derived by deconvolution suggest that the synchronous release component is not affected at SynII(−) slices. Dotted lines indicate confidence interval for the cumulative synchronous release. Inset, Total synchronous release over the duration of the tetanus. H, The asynchronous release component computed using deconvolution. Right, Plot (overlay) represents the data normalized by the first response in a tetanus. I, The cumulative asynchronous release component is significantly reduced at SynII(−) slices. Dotted lines indicate the confidence interval. Inset, Total asynchronous release, including that recorded during and after the tetanus (p < 0.01). J, The ratio between the cumulative asynchronous and synchronous release components is significantly reduced at SynII(−) slices (p < 0.01). Data collected from 26 slices for each genotype. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.005, ****p < 0.001.
