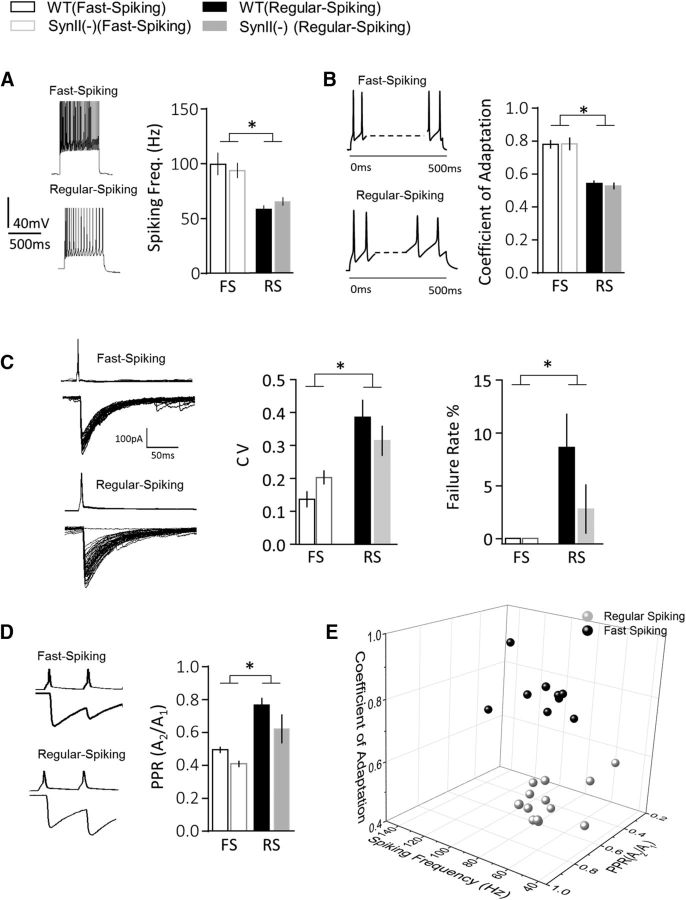
Figure 5.
Perisomatic interneurons with fast IPSC kinetics constitute two interneuron subtypes, FS and RS. All the connected pairs are classified according to five parameters: SF (A), CA (B), CV (C), FR (C), and PPR (D). *Significant difference (p < 0.05) between the interneuron subtypes (two-way ANOVA). A, Spiking frequencies differ between neuron subtypes but not between the genotypes. B, RS interneurons have a lower CA, which is manifested as a stronger decay in SF. C, RS interneurons have a higher variability in IPSC amplitudes, CV, and a higher failure rate. D, RS interneurons have a higher PPR. E, A 3D plot showing that all the interneuron subtypes fell into two distinct clusters according to three physiological parameters: SF, CA, and PPR. WT and SynII(−) genotypes were pooled together because all the plotted parameters were similar for WT and SynII(−) lines.