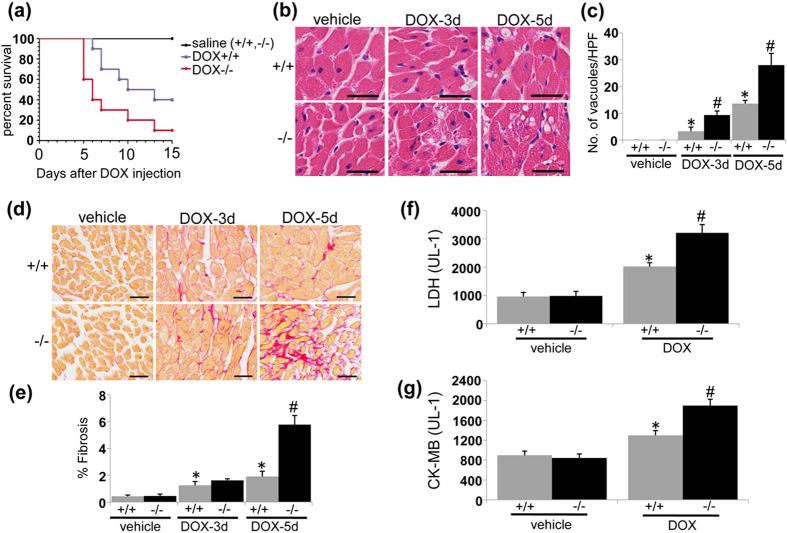
Figure 1. UVRAG deficiency exacerbates acute DOX-induced cardiotoxicity.
(a) Survival curves of WT and UVRAG-deficient mice after acute DOX treatment were created by Kaplan-Meier method (*P < 0.05 using the Log-rank test). n = 7 mice for saline+/+, n = 8 mice for saline−/−, n = 10 mice for DOX+/+, n = 10 mice for DOX−/−. (b) Representative H&E images of degenerative vacuoles in LVs on heart sections from WT and UVRAG-deficient mice 3 or 5 days after acute DOX or vehicle treatment. Scale bar: 40 μm. (c) Quantification of degenerative vacuoles in LVs in the experiments as illustrated in (b). n = 3 mice for each group. (d) Representative images of fibrosis stained with picrosirius red in LVs on heart sections from WT and UVRAG-deficient mice 3 or 5 days after acute DOX or vehicle treatment. Scale bar: 40 μm. (e) Quantification of fibrosis in LVs in the experiments as illustrated in (d). n = 3 mice for each group. (f) Serum LDH activity in WT and UVRAG-deficient mice 3 days after acute DOX or vehicle treatment. n = 4 mice for each group. (g) Serum CK-MB activity in WT and UVRAG-deficient mice 3 days after acute DOX or vehicle treatment. n = 4 mice for each group. *P < 0.05 vs. WT + vehicle, #P < 0.05 vs. WT + DOX.