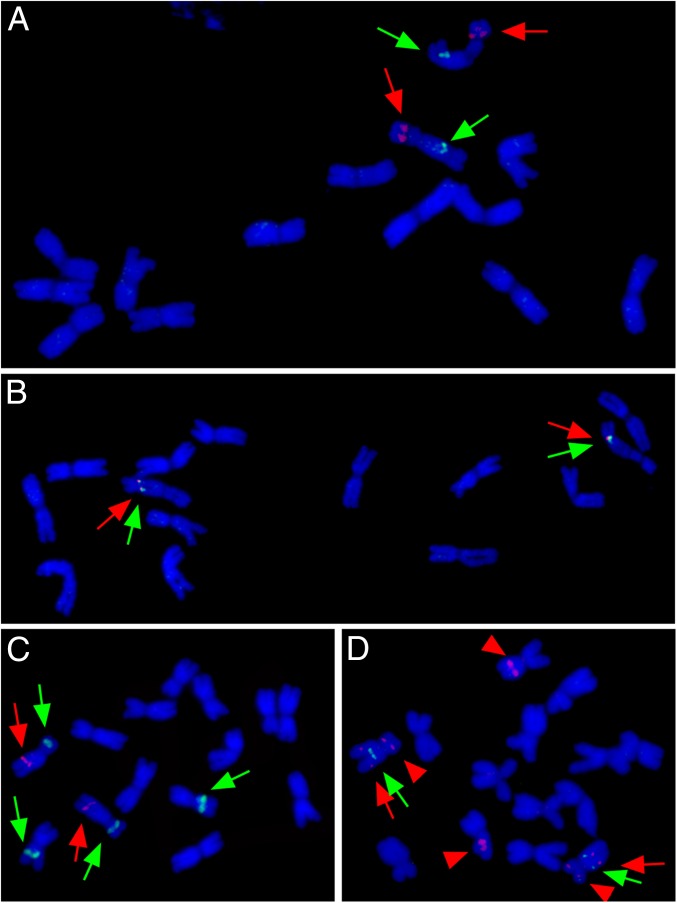
Fig. 3.
Molecular cytogenetic analysis of (A and B) H. bogdanii and (C and D) H. pubiflorum. (A) The BAC clone 46L9 signal (green arrows) localizes to a site on the long arm of the same chromosome that carries the 45S-rDNA cluster (red arrows). (B) The BAC clone 46L9 signal (green arrows) colocalizes with the signal obtained from the P. bergii genomic DNA probe (red arrows) to a site on a single chromosome pair. (C) The signal obtained from the P. bergii genomic DNA probe (red arrows) localizes to a site on the long arm of the same chromosome that carries one of two native rDNA clusters present (green arrows). (D) The signal obtained from the Pa. dilatatum genomic DNA probe (green arrows) highlights a site proximal to one hybridizing to P. bergii genomic DNA (red arrows). The red arrowheads show the native rDNA clusters.