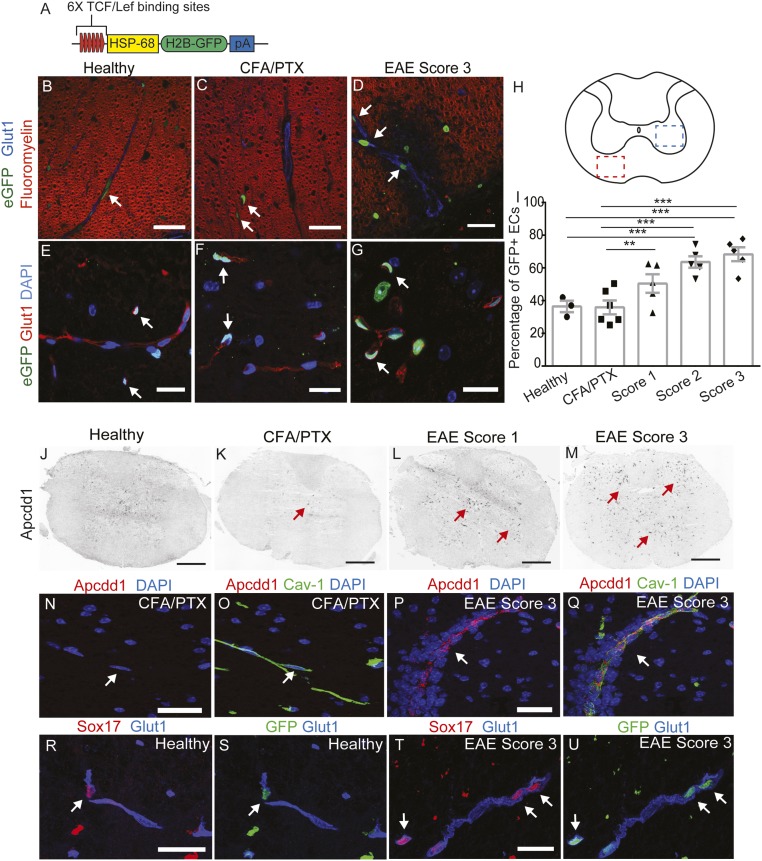
Fig. 1.
The Wnt/β-catenin pathway is up-regulated in thoracic spinal cord ECs during EAE. (A) Diagram of the TCF/LEF1::H2B-eGFP Wnt reporter transgene. (B–H) Immunofluorescence for eGFP (green), fluoromyelin (myelin; red), and Glut-1 (blood vessels; blue) in the white matter of thoracic spinal cords from the Wnt reporter strain. Wnt activity (eGFP immunofluorescence) is increased in white matter thoracic spinal cord ECs (H, red square; B–D, white arrows) during EAE progression. Wnt reporter activity is also increased in ECs in the gray matter of thoracic spinal cords during EAE progression (H, blue square; E–G, white arrows). Glut-1 (red) labels blood vessels, and DAPI indicates nuclei. (I) Quantification of Wnt reporter activity in thoracic spinal cord ECs during EAE progression. Healthy, n = 3; CFA/PTX, n = 6; EAE score 1–3, n = 5. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, mixed-effects ANOVA. (J–M) In situ hybridization for Apcdd1 during progression of EAE in thoracic spinal cords. Apccd1 mRNA levels are increased at EAE scores 1 and 3 (red arrows). (N–Q) In situ hybridization for Apcdd1 (red) combined with immunofluorescence for Cav-1 (blood vessel marker; green) in CFA/PTX controls and EAE score 3. Apcdd1 mRNA is up-regulated during EAE progression and colocalizes with Cav-1. (R–U) Immunofluorescence for Sox17 (red), eGFP (green), and Glut-1 (blue) in healthy and EAE score 3 thoracic spinal cords. Sox17 is up-regulated in the vasculature during EAE, and colocalizes with eGFP in Wnt reporter mice (white arrows). (Scale bars: 20 μm; 200 μm in J and K).