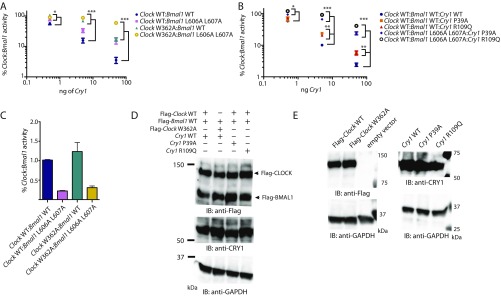
Fig. S2.
Point mutations in CLOCK PAS-B and CRY1 secondary pocket reduce repression of Clock:Bmal1 by Cry1. (A) Per1-Luc assay with increasing amounts of plasmids encoding mCry1 (0.5, 5, and 50 ng) with Clock wild-type or Clock W362A and Bmal1 WT or L606A L607A (100 ng each). Relative activity normalized to Clock:Bmal1 (wild-type or mut) without mCry1 cotransfected set to 100. (B) Per1-Luc assay with increasing amounts of mCry1 wild-type or point mutants (P39A and R109Q) with Clock wild-type and Bmal1 wild-type or L606A L607A. L606A and L607A mutations in the transactivation domain of Bmal1 reduce repression by mCry1 and synergistically reduce repression when paired with mutations in CLOCK PAS-B and the CRY1 secondary pocket. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared by two-tailed t test. (C) Comparison of relative activity of Clock:Bmal1 constructs used in Per1-luciferase assay. The basal activity of the mutants are shown relative to wild-type Clock:Bmal1 activity set to 1.0. (D) HEK293T cells were transfected with plasmid ratios used in Per1-luciferase assay (100 ng each Flag-Clock and Flag-Bmal1, and Cry1 plasmid as indicated, scaled 4× for increase in culture dish area). Relative protein expression levels are shown by Western blotting using indicated antibodies. GAPDH is shown as a loading control. (E) HEK293T cells were transfected with 1 μg of the indicated plasmid. Relative protein expression levels are shown by Western blotting using indicated antibodies.