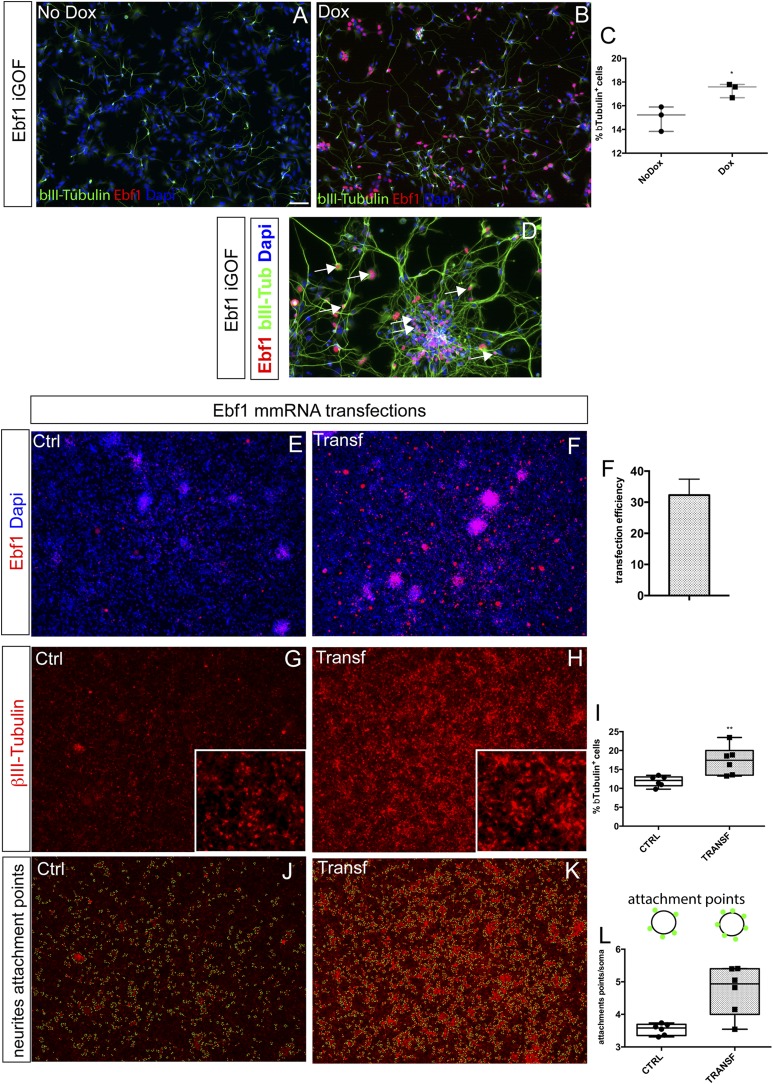
Fig. S5.
Ebf1 enhances neuronal differentiation in hES-derived neural progenitors. (A and B) Representative images of day 30 neuronal monolayers generated from Ebf1 iGOF hES line in basal conditions (A) and after 10 d of doxycycline treatment (B) showing bIII-Tubulin (green) and Ebf1 (red) expression. (C) Graph shows quantification of βIII-Tubulin+ cells in the two conditions. Center lines show the average; whiskers indicate minimum and maximum. (D) Higher magnification of Ebf1+bIIITubulin+ cells in Ebf1 iGOF cells. (E–I) Ebf1 mmRNA transfections of H9 hES-derived neural progenitor cells. (D and E) Representative images of day 30 neuronal monolayers generated from H9 hES cells transfected with 200 ng of Ebf1 mmRNA, showing Ebf1 overexpression (red). (F) Quantification of Ebf1+ cells 48 h after transfection. (G and H) Representative images of βIII-Tubulin expression of neuronal monolayers in control cells (G) and after 5 d of Ebf1 mmRNA transfections (H). (I) Quantification of βIII-Tubulin+ neurons. Center lines show the average; whiskers indicate minimum and maximum. (J–L) Neurite attachment point quantification of βIII-Tubulin staining performed in G and H. (L) Graph shows attachment point quantification by NeurphologyJ software. Box shows the median and the 25th and 75th percentiles. The whiskers of the graph show the largest and smallest values. (Scale bar, 100 μm.) *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005.