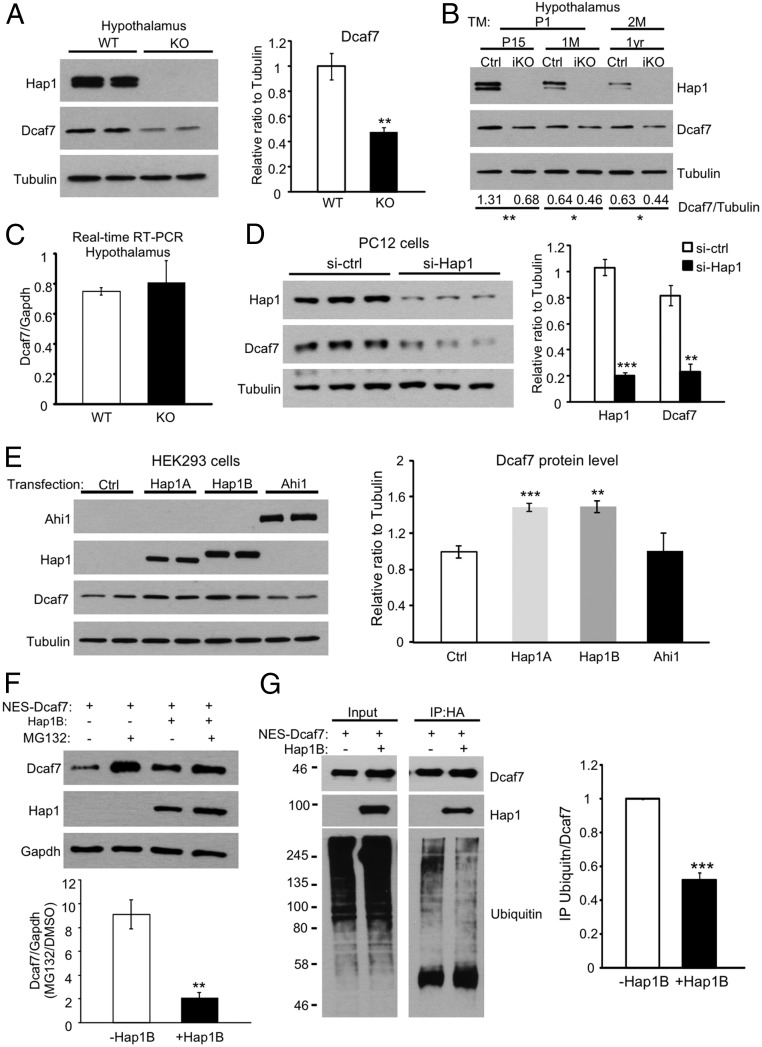
Fig. 4.
Hap1 stabilizes Dcaf7 in the cytoplasm by reducing its proteasome degradation. (A) Western blotting shows a significant reduction in Dcaf7 protein level in Hap1-KO mouse hypothalamus. Ratios were normalized to WT. n = 4 each. (B) Decreased Dcaf7 levels also were observed in the hypothalami of postnatal day 15/1-mo-old induced Hap1-KO (iKO) mice injected with tamoxifen for 3 d beginning at postnatal day 1 or of 1-y-old iKO mice injected with tamoxifen for 5 d beginning at 2 mo of age. The ratios of Dcaf7 to tubulin were obtained from three independent experiments and are shown beneath the blots. (C) Real-time RT-PCR found no difference in Dcaf7 mRNA levels in hypothalami from postnatal day 2 WT and Hap1-KO mice. n = 4 per group. (D) Knockdown of Hap1 using siRNA in PC12 cells drastically down-regulated Dcaf7. Ratios were normalized to the control level. n = 3 per group. (E) Transfections of Hap1A or Hap1B, but not Ahi1, increased the endogenous Dcaf7 levels in HEK293 cells. Ratios were normalized to the control level. n = 4 per group. (F) HEK293 cells treated with 5 µM MG132 for 16 h showed more NES-Dcaf7 accumulation without Hap1B than when Hap1B was cotransfected. n = 3 per group. (G) Hap1B cotransfection with NES-Dcaf7-HA reduces the polyubiquitination of Dcaf7. NES-Dacf7-HA was immunoprecipitated by anti-HA. Ratios were normalized to the NES-Dcaf7-HA–only group. n = 3 per group. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.