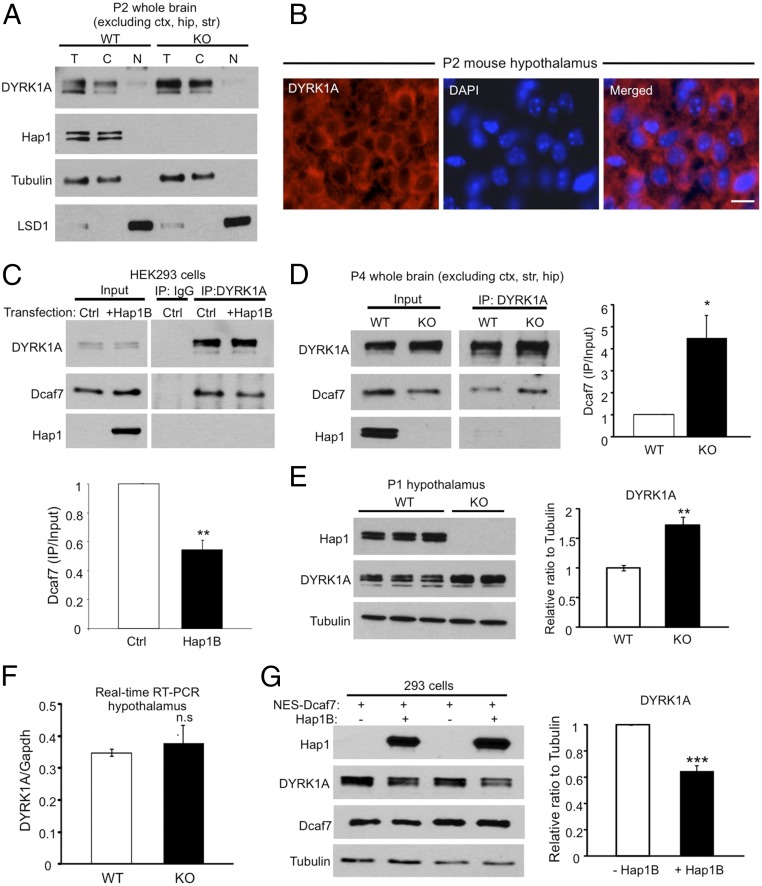
Fig. 5.
DYRK1A and Hap1 compete for Dcaf7 binding in the cytoplasm, and the protein level of DYRK1A is increased in Hap1-KO mouse brains. (A) Fractionation of postnatal day 2 mouse brains reveals a preponderantly cytoplasmic distribution of DYRK1A. T, total; C, cytoplasmic; N, nuclear. (B) Immunostaining of DYRK1A in postnatal day 2 mouse hypothalamus also demonstrates cytoplasmic localization of DYRK1A. (Scale bar: 10 µm.) (C) Hap1B expression significantly reduces the interaction between DYRK1A and Dcaf7 in HEK293 cells. Ratios were normalized to control level. n = 3 each. (D) The association between DYRK1A and Dcaf7 is dramatically enhanced in Hap1-KO mouse brains. Ratios were normalized to the WT level. n = 3 per group. (E) The protein level of DYRK1A is increased in postnatal day 1 Hap1-KO hypothalamus. Ratios were normalized to WT level. n = 4 each. (F) Real-time RT-PCR found no difference in DYRK1A mRNA levels in postnatal day 2 WT and Hap1-KO mouse hypothalami. n = 4 per group. (G) The expression of transfected NES-Dcaf7 was adjusted at similar levels in groups with or without Hap1B cotransfection in HEK293 cells. The presence of Hap1B reduces the level of endogenous DYRK1A. Ratios were normalized to the NES-Dcaf7–only group. n = 3 per group. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001, n.s., not significant.