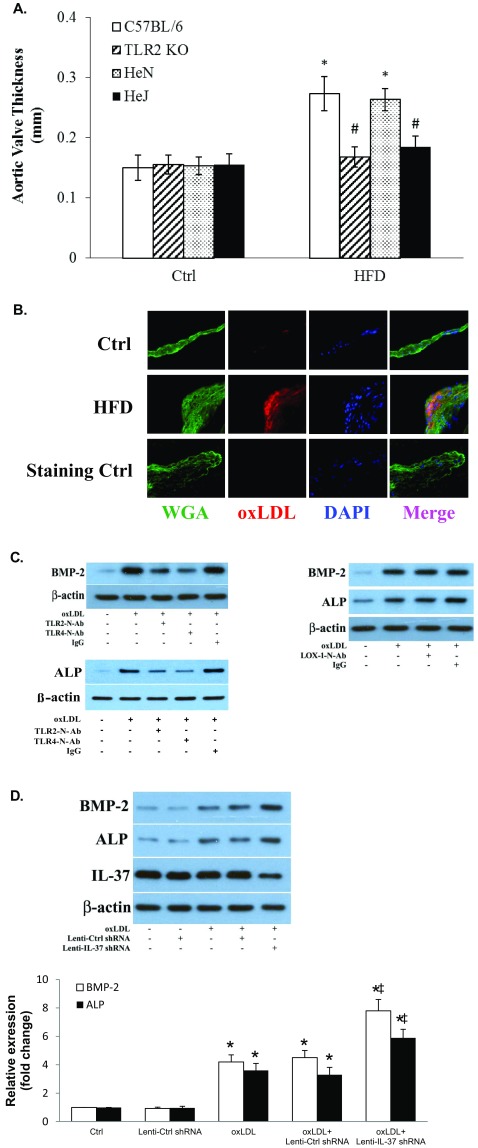
Fig. S4.
(A) Both TLR2 and TLR4 are involved in mediating aortic valve thickening caused by high fat diet (HFD). C57BL/6 (WT) mice, TLR2 knockout (TLR2 KO) mice, C3H/HeN (HeN, TLR4 competent) mice, and C3H/HeJ (HeJ, TLR4-defective mutant) mice were fed with a HFD (45% fat as in kcal%) for 16 wk. Quantification data from ultrasound analysis show that either TLR2 KO or TLR4 mutation attenuates aortic valve thickening caused by HFD. n = 10 in each group, *P < 0.05 vs. control, #P < 0.05 vs. C57BL/6 HFD or HeN HFD. (B) HFD causes oxLDL deposition in aortic valve leaflet. C57BL/6 (WT) mice fed with a HFD (45% fat as in kcal%) for 12 wk. A representative immunofluorescence image shows oxLDL accumulation in aortic valve tissue. (Original magnification: 40×.) (C) OxLDL induces the osteogenic responses through TLR2 and TLR4, not LOX-1. AVICs of normal aortic valves were treated with oxLDL (40 µg/mL) for 3 d in the absence or presence of a neutralizing antibody against TLR2, TLR4, or LOX1. Representative immunoblots show reduced levels of BMP-2 and ALP in AVICs treated with either anti-TLR2 or anti-TLR4, but not in cells treated with anti-LOX1. (D) IL-37 knockdown augments AVIC osteogenic responses to oxLDL. Human AVICs were treated with lentiviral IL-37 shRNA before being exposed to oxLDL (40 µg/mL) for 3 d. Representative immunoblots and densitometric data (n = 5) show that IL-37 KD augments BMP-2 and ALP expression in response to oxLDL. *P < 0.05 vs. corresponding control; ‡P < 0.05 vs. oxLDL or oxLDL+Ctrl shRNA.