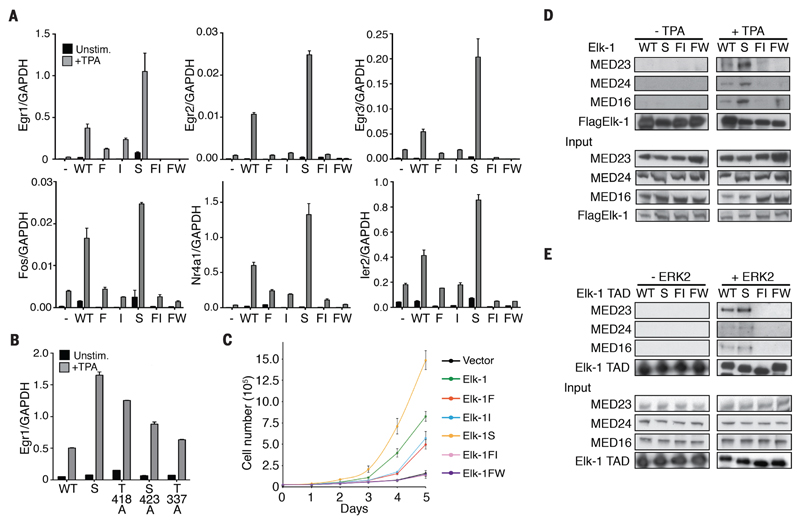
Figure 3. Effects of Elk-1 TAD mutations on TCF target gene expression, cell proliferation and Mediator binding.
(A) Quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) analysis of TCF target gene transcription in reconstituted TKO MEFs. Cells were reconstituted with wild-type mouse Elk-1 (WT) or fast-site (F), intermediate-site (I), slow-site (S), fast- and intermediate-site (FI) or alanine-substituted FW motif (FW) mutants. (B) Effects of individual slow-site alanine substitutions on Egr1 expression. In (A) and (B) cells were stimulated with 50 ng/ml TPA where indicated. RNA levels are quantified relative to GAPDH; data are means ± SEM, n = 3. (C) Proliferation of wild-type and mutant Elk-1 TKO MEFs. Data are means ± SEM, n = 3. (D) Co-immunoprecipitation of Mediator with wildtype or mutant Flag-tagged Elk-1 from NIH3T3 cell extracts. Antibodies to Mediator subunits MED23, MED24 and MED16 were used for immunoblotting. (E) Mediator co-precipitation from unstimulated NIH3T3 cell extracts using wild-type and mutant GST-tagged Elk-1 TAD proteins with and without prior ERK2 phosphorylation.