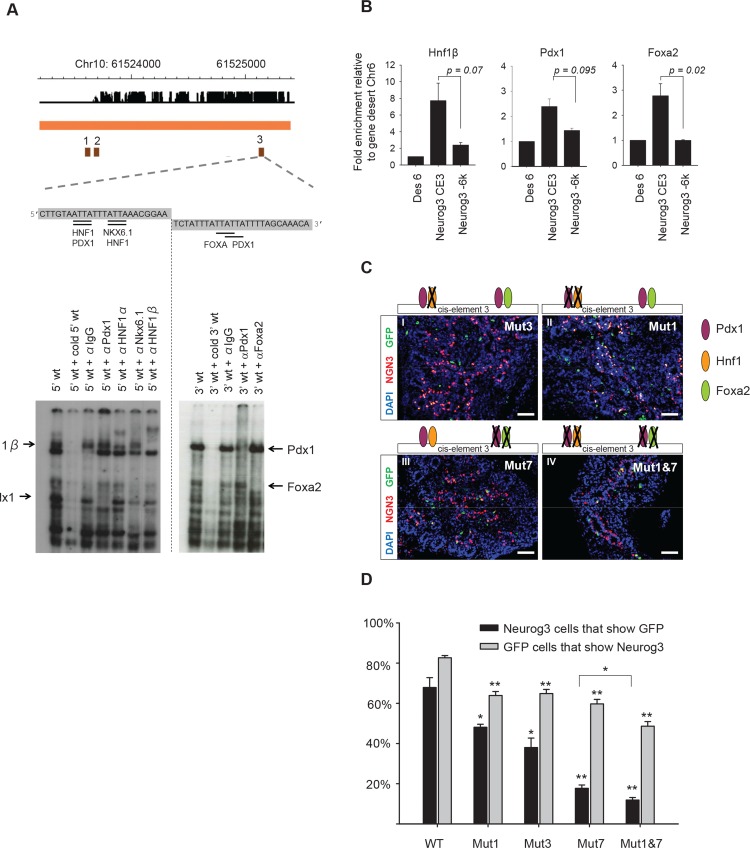
Fig 3. Identification of cis-regulatory mutations that disrupt activation of Neurog3 in pancreatic progenitors.
A. Binding of Hnf1b, Pdx1 and Foxa2 to cis-element 3 of the Neurog3 enhancer using EMSAs with nuclear extracts from E13.5 pancreatic buds. The 5’ part of the cis-element 3 sequence binds Hnf1b and Pdx1 while the 3’ part binds Pdx1 and Foxa2. B. ChIP for Hnf1b (n = 3), Pdx1 (n = 2) and Foxa2 (n = 3) in E13.5 pancreatic buds. Binding to the cis-element 3 (Neurog3 CE3) was compared to control regions Des6 (locus in gene-desert) and Neurog3 -6K (Neurog3 5’ upstream region). Indicated P-values were calculated with Students t-test. C. Lentiviral transgenesis using enhancers with indicated mutations, all of which disrupt specific transcription factor binding sites (S3 Fig). Note how the strongest reduction of expression is found upon disruption of all identified binding sites within cis-element 3. D. Quantification of percentage of Neurog3 cells that are GFP positive (black bars) and the percentage of GFP cells that are Neurog3 positive (grey bars). Quantification was done on 8 embryos for each genotype in which at least 1000 Neurog3 cells were counted ([**] P<1.0 x 10−6, [*] P<0.02, Student’s t-test with Bonferroni correction). Scale bars: C I-VI = 50 μm.