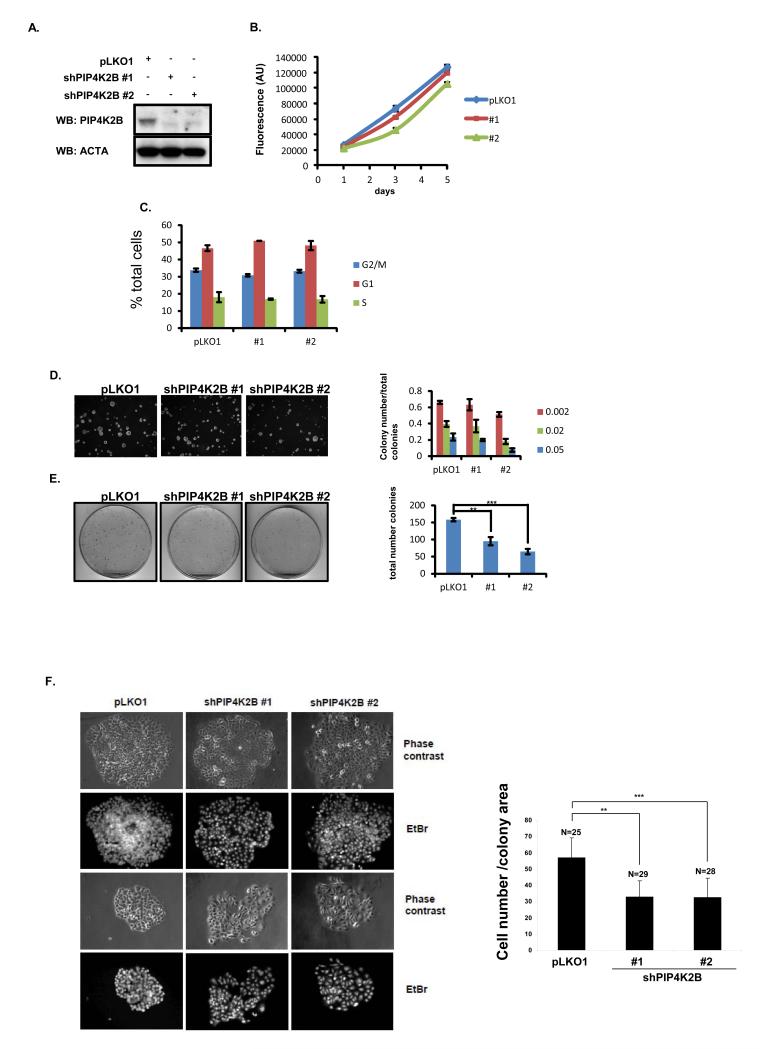
Figure 4.
PIP4K2B knock down in MCF7 does not affect normal cell growth, cell cycle distribution or growth in soft agar, but decreases anchorage-dependent clonogenic growth. MCF7 cells were transduced with a control lentiviral vector or two different shRNA vectors targeting PIP4K2B (#1 and #2) and then analysed as below. A. Cell lysates were subjected to western blotting to detect PIP4K2B and actin. B, MCF7 cells were plated and viability/proliferation was measured on days 1, 3 and 5 post plating using alamar blue. Data are representative of three experiments and represent the mean ± SD. C. Cells were fixed and labelled with propidium iodide and analysed by FACS. D. MCF7 cells were plated in soft agarose to assess anchorage-independent growth. The graph presents the numbers of three different sizes of colonies (Image J Arbitrary Units, from small 0.002 to big 0.05) divided by the total number of colonies. Data are representative of two experiments performed in triplicate and the data represent the mean ± SD. E. 1000 MCF7 cells were plated in a 10 cm plate and grown for 10 days. Typical images of the colonies are shown and quantification of colony number showed significant differences (** P <0.01, *** P <0.001 (student t-test)) between pLKO and PIP4K2B knockdown constructs (#1 and #2). F. Colony density from E was evaluated by staining cell nuclei with ethidium bromide (EtBr) to assess cell number per colony and phase contrast images were used to determine the colony area The data are presented as the number of cells per colony surface area (Image J, arbitrary units). ** P <0.01, *** P <0.001 (Students t-test).