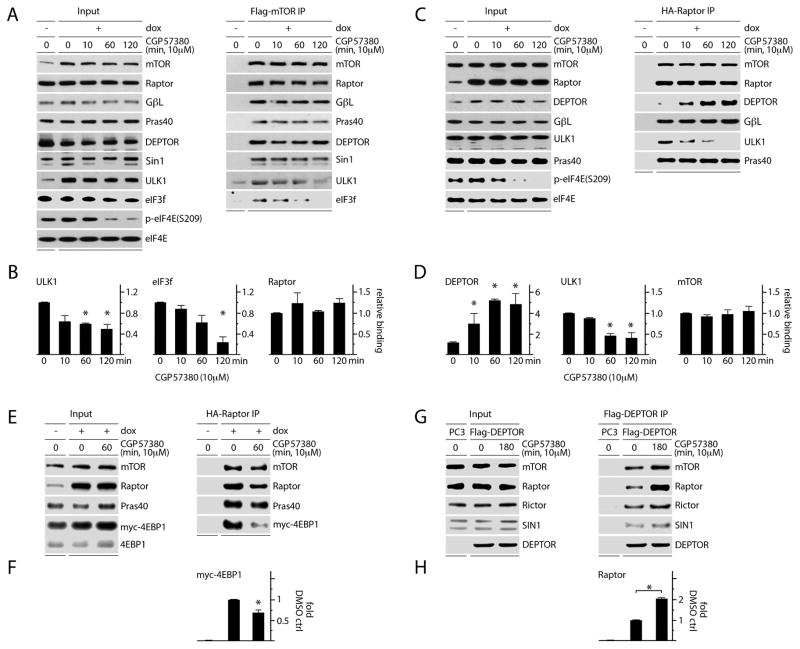
Figure 3. MNK inhibition reduces mTORC1 association with its substrates and increases DEPTOR association with mTORC1.
(A, B) Dox-inducible Flag-mTOR expressing HEK293 cells were treated with mock (DMSO) or CGP57380 as shown. Lysates were subjected to Flag-IP and immunoblot; Raptor, ULK1, and eIF3f binding levels are quantitated in (B).
(C) Dox-inducible HA-Raptor expressing HEK293 cells were treated as in (A) and lysates were subjected to HA-IP and immunoblot. Quantitation of DEPTOR, ULK1 and mTOR binding is shown in (D).
(E) Dox-inducible HA-Raptor expressing HEK293 cells were transfected with myc-4EBP1, treated with DMSO or CGP5780, harvested, and the lysates used for HA-IP and immunoblot to detect co-IP of myc-4EBP1 with Raptor. HA-Raptor:myc-4EBP1 co-IP was quantitated (F).
(G) HEK293 cells were transfected with Flag-DEPTOR, treated with DMSO or CGP57380, and subjected to Flag-IP and immunoblot to detect changes in mTORC1 vs. C2 interactions; Flag-DEPTOR:Raptor co-IP was quantitated (H).
(B, D, F, H) Quantitation of immunoblot signals represent the average of 3 (B, D, F) or 2 (H) independent experiments. The values were normalized to the mock (DMSO), dox-induced control.