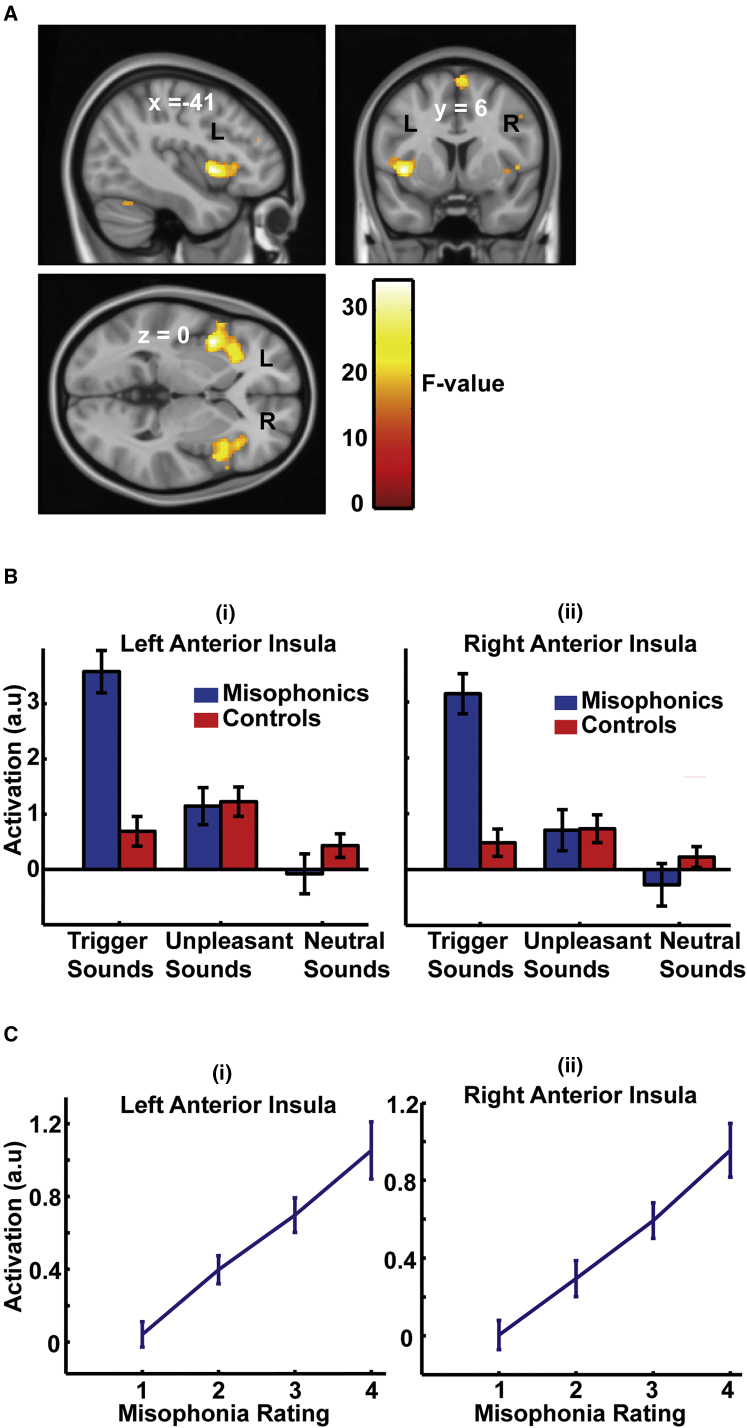
Figure 2.
Group-Level, Random-Effects GLM Analysis of fMRI Data
The GLM was modeled as a factorial design with group (two levels) and sound types (three levels) as factors.
(A) Statistical parameter maps (SPMs) overlaid on a standard MNI-152 template brain for the critical interaction between the two factors (group and sound type) thresholded at p = 0.05 family-wise error (FWE) corrected for whole-brain volume. The effect is maximal in AIC (bilateral) with maxima at MNI coordinates (−41, 6, 0).
(B) Confirmatory plots of activity averaged over cluster in AIC (see also Figures S1 and S2 and Table S1) show that the interaction effect was driven by higher activity for trigger sounds in misophonic subjects compared to controls.
(C) Confirmatory plots of activity in AIC with misophonic ratings in misophonic subjects.
Data in (B) and (C) show mean (± SEM).