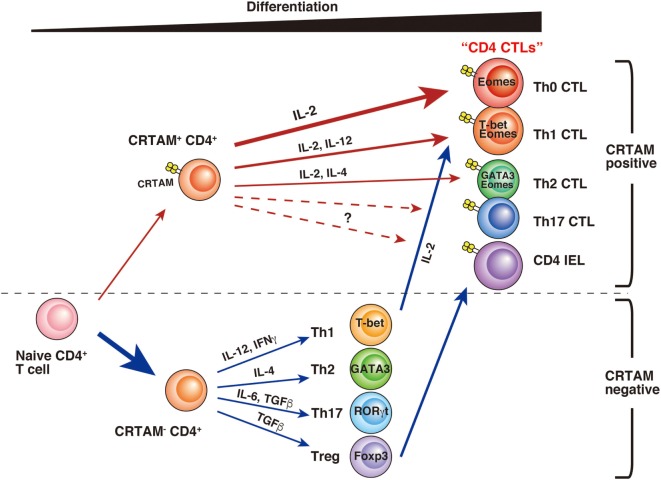
Figure 1.
A model of CD4 CTL differentiation. After T cell receptor stimulation, a small fraction of naïve CD4+ T cells express class I-restricted T cell-associated molecule (CRTAM). CRTAM+ CD4+ T cells have the potential to differentiate into CD4 CTLs, which gain cytotoxic activity after incubation with IL-2 (Th0 CTL). Under the cultivation in the skewed conditions for each Th subset, they differentiate into Th1- or Th2-like cells with cytotoxic function (Th1 CTL, Th2 CTL). On the other hand, the majority of CRTAM− CD4+ T cells can differentiate into various Th subsets based on environmental cytokines. Th1 polarized CD4+ T cells are known to show cytotoxic activity, and it has recently shown that intestinal regulatory T cells (Treg) can convert to cytotoxic CD4 intraepithelial lymphocytes.