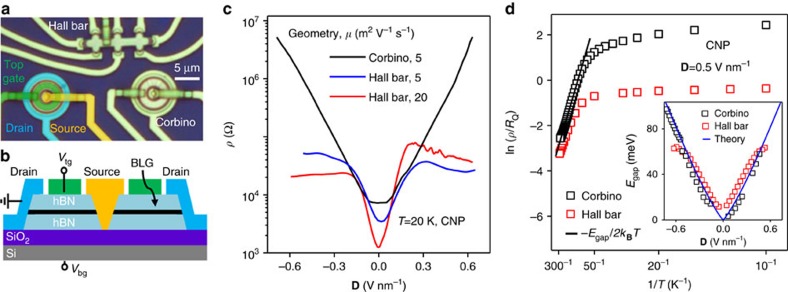
Figure 4. Charge-neutral bilayer graphene in the Corbino and Hall bar geometries.
(a) Optical image of one of our devices with a Hall bar and two Corbino disks. The left-disk image is coloured to indicate source, drain and top gate electrodes. (b) Cross-sectional schematic of our double-gated Corbino devices. (c) Resistivity ρ at the CNP for Corbino and Hall bar geometries as a function of D. For the Corbino device, ρ changes exponentially over three orders of magnitude. The Hall bars exhibit saturation to a few RQ. (d) Arrhenius plot for ρ(T). The energy gap Egap is calculated from the linear slopes at T>100 K, which are similar for both Corbino and Hall bar geometries. Below 50 K, the Hall bar device exhibits little T dependence. Inset: Egap found for various D (symbols). The blue curve is tight-binding calculations for the BLG gap from ref. 3.