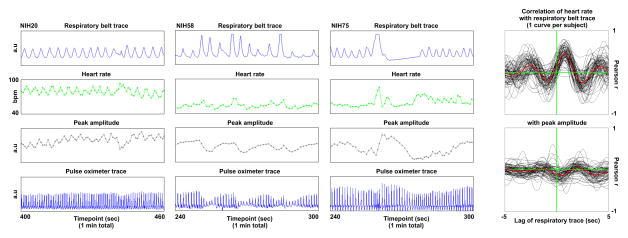
Figure 5. Relationships between respiratory cycles, estimated heart rate, and pulse pressures.
For 1 minute of data from 3 subjects, top and bottom panels show respiratory belt and pulse oximeter traces (both 50 Hz signals). Instantaneous heart rate is calculated from the peak-to-peak interval and plotted in green at the peak time, as is peak amplitude. Cyclical influences of respiration on heart rate and peak amplitude are evident. Such traces can be seen for all subjects in Videos 3a and 3b. The black traces at right show the correlation between respiratory belt traces and heart rate and peak amplitude, with -5 to 5 seconds of lag applied to the respiratory trace.