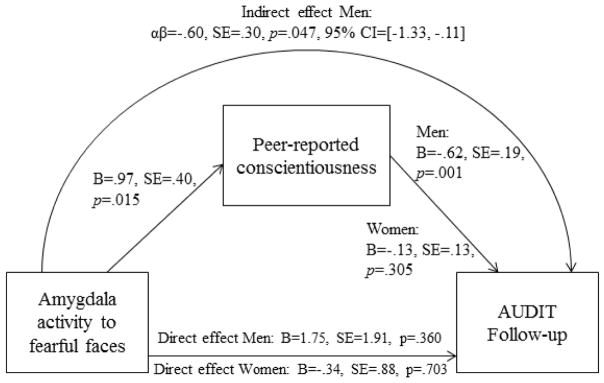
Figure 4. Indirect effect of amygdala activity to fearful facial expressions on future problem drinking in men via peer-reported conscientiousness.
The indirect effect was modeled using a multi-group model with participant sex as the grouping factor. The association between amygdala activity and peer-reported conscientiousness was constrained to be equal between men and women, given no significant moderation. The effect of peer-reported conscientiousness on AUDIT follow-up scores was freed to vary between men and women, given evidence for significant moderation. Accordingly, the indirect effect was estimated separately for men and women. 95% CI=95% bias-corrected bootstrapped confidence intervals.