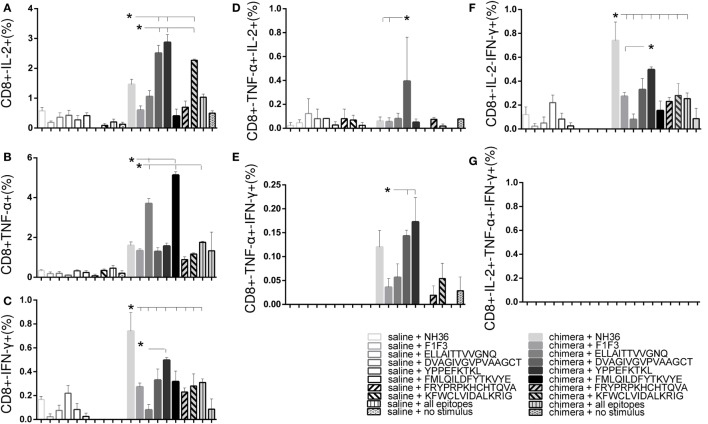
Figure 10.
Multiparameter cytometry analysis disclosed that the YPPEFKTKL followed by the DVAGIVGVPVAAGCT, FMLQILDFYTKVYE, and ELLAITTVVGNQ epitopes induced the most potent CD8+ T cell response. Splenocytes of chimera-vaccinated mice were incubated with NH36, the chimera, the ELLAITTVVGNQ, DVAGIVGVPVAAGCT, YPPEKTKL, FMLQILDFYTKVYE, FRYPRPKHCCHTQVA, and KFWCLVIDALKRIG sequences, or with the mixture of all the epitopes, at week 11 after infection. The magnitude of the CD4+ T cell response was disclosed by the frequencies of the CD4+ lymphocytes expressing IL-2 (A), TNF-α (B), IFN-γ (C), IL-2/TNF-α (D), TNF-α/IFN-γ (E), IL-2/IFN-γ TNF-α/IFN-γ (F), and IL-2/TNF-α/IFN-γ TNF-α/IFN-γ (G) in response to each antigen. Bars represent means + SE of two independent experiments, each one with 8–10 animals per treatment. YPPEFKTKL was the most potent epitope. Alone, it induced higher proportions of CD8+ T cells secreting IFN-γ and IFN-γ in combination with IL-2 than the chimera; together with DVAGIVGVPAAGCT and KFWCLVIDALKRIG, the highest frequencies of CD8+-IL-2 T cells and combined only with DVAGIVGVPAAGCT, the highest proportions of CD8+-TNF-α-IFN-γ T cells. In addition, DVAGIVGVPAAGCT increased the frequencies of CD8+-TNF-α-IL-2 T cells. In contrast, ELLAITTVVGNQ and the FMLQILDFYTKVYE epitopes increased the frequencies of T cells secreting only TNF-α.