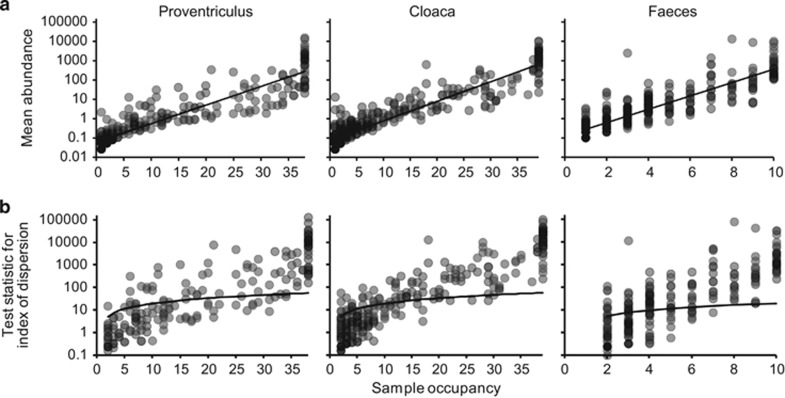
Figure 1.
Distribution and dispersal of bacterial taxa among the proventriculus, cloacal and faecal microbiomes. (a) The number of samples for which each detected bacterial taxon was observed, plotted against the mean sequence abundance (log10 scale) of that taxon among all samples within each microbiome (proventriculus, r2=0.75, F1,289=855.5, P<0.0001; cloaca, r2=0.82, F1,407=1797.6, P<0.0001; and faeces, r2=0.71, F1,332=780.1, P<0.0001). (b) A dispersal plot to identify which bacterial taxa are randomly distributed within each microbiome, a measure used to assign core versus satellite status. Index of dispersion was calculated as the ratio of variance to mean of abundance for each taxon within each cohort and plotted for each sample. The line depicts the 2.5% confidence limit for the χ2 distribution. Taxa that fall below this line are randomly distributed and were considered satellite taxa, whereas those that are above the line are non-randomly distributed and were considered core taxa. The 97.5% confidence limit was not plotted, as no taxa fell below that line.