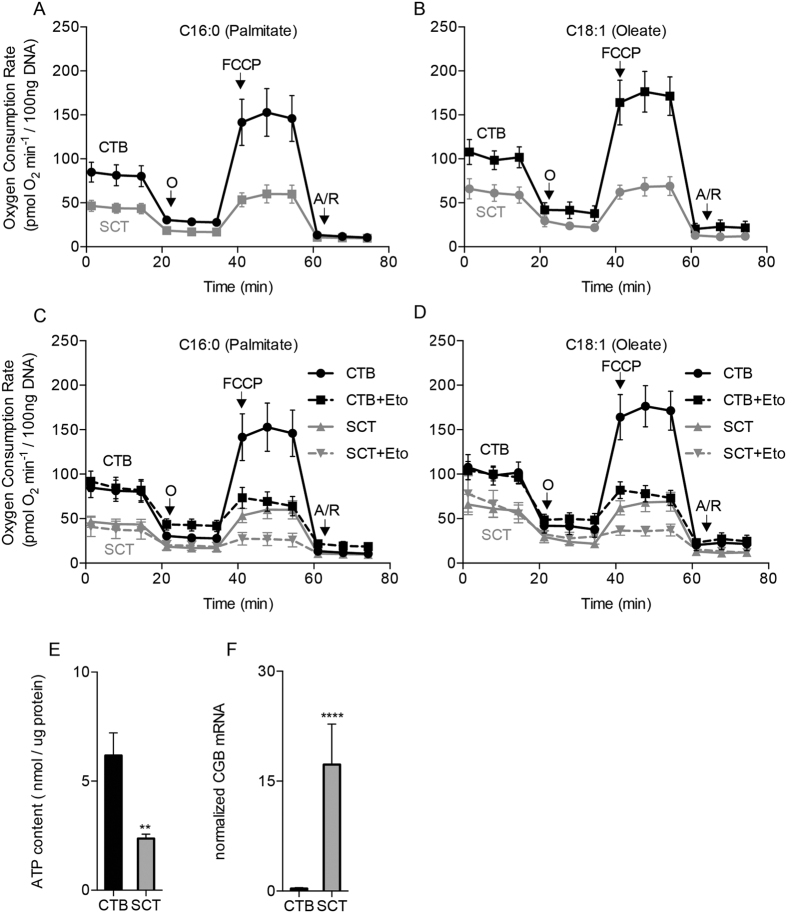
Figure 2. Human trophoblast respiration rates.
Human cytotrophoblast cells (CTB) were isolated from term placentas and studied in vitro before and after differentiation into syncytiotrophoblast (SCT). (A,B) Respiration was measured in Krebs-Henseleit buffer containing 250 μM of either saturated long-chain fatty acid palmitate (C16) or the monounsaturated oleate (C18) using the Seahorse XF Analyzer. Oxygen consumption rate (OCR) was greater in CTB than in SCT at baseline (0 to15 min), at maximal oxidative phosphorylation with FCCP (40–60 min) and at all other points during a standard mitochondrial stress protocol. (C,D) Etomoxir, an inhibitor of carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1 (CPT1a), reduced maximal OCR, measured after FCCP injection, in both CTB and SCT for both fatty acids but not at baseline. (E) Resting ATP levels were also much higher in CTB than in SCT. (F) We measured the SCT marker, chorionic gonadotropin beta (CGB) and showed that it was highly expressed at the 72 hr time point (SCT) but not at 8 hr (CTB). Oligomycin (O), Antimycin/Rotenone (A/R). Data are Mean ± SEM, n = 7 placentas.