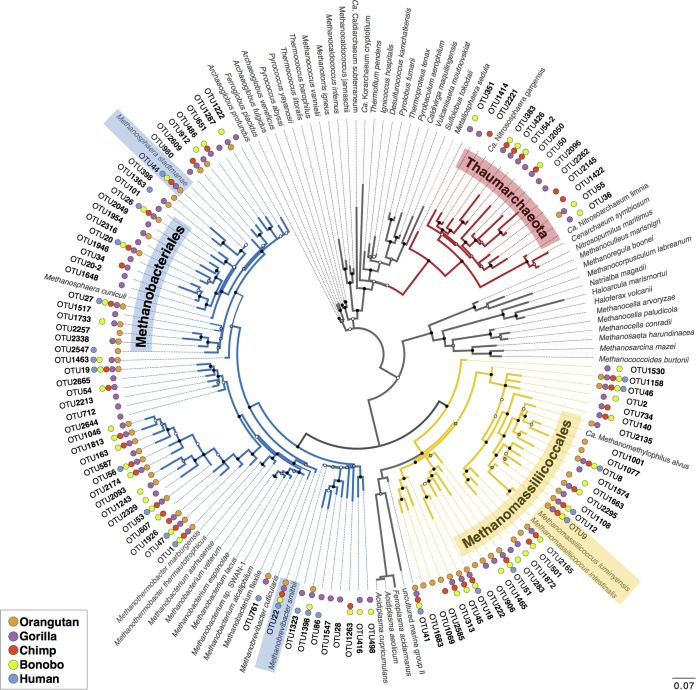
FIG 3 .
Phylogenetic diversity of archaeal lineages in the great ape gut microbiome. Shown is an unrooted maximum likelihood tree of 102 archaeal 94% OTUs detected in great apes (numbered OTUs) and 58 archaeal 16S reference sequences (Latin binomes). Phylogeny was inferred by PhyML (GTR+Γ4). Colored branches denote the major three archaeal groups to which all identified OTUs belong: Methanobacteriales (blue), Methanomassiliicoccales (yellow), and Thaumarchaeota (red). OTUs identical or with very high similarity to archaeal strains previously identified in the human gut microbiome are highlighted: M. smithii and M. stadtmanae in blue and M. luminyensis and “Ca. Methanomassiliicoccales alvus” in yellow. Solid circles at branch termini show the OTU distribution among host species, with OTUs considered present if found in any individual of a species. The scale bar represents the average number of substitutions per site. Reliability of internal branches was assessed by bootstrapping (100 replicates) and the approximate likelihood ratio test (aLRT–SH-Like). Dots at nodes denote aLRT values: black, >0.8; gray, >0.5; white, < 0.5.