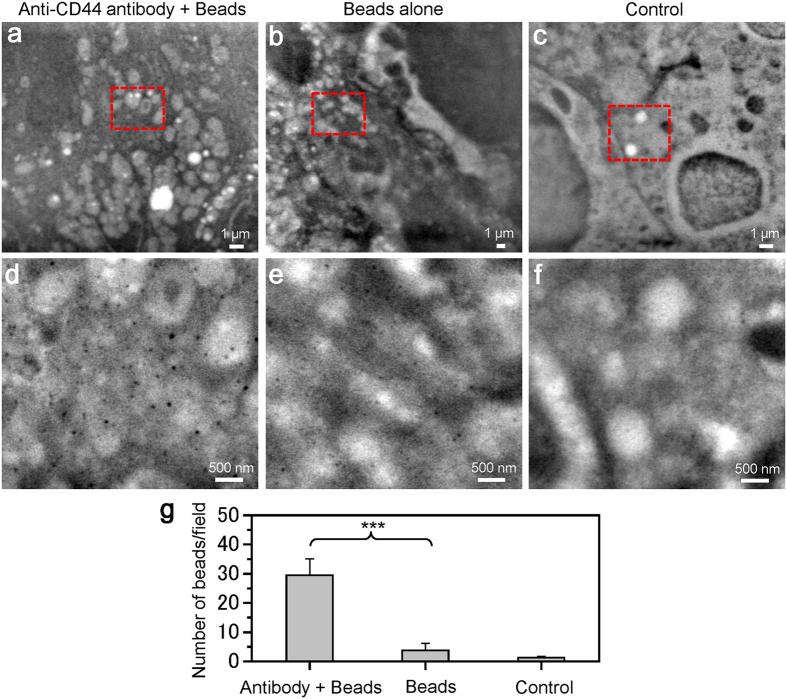
Figure 4. SE-ADM images of nanobeads binding to cancer cells via anti-CD44 antibodies.
(a) An image of the streptavidin-conjugated 100-nm beads binding to cells via biotin-conjugated anti-CD44 antibodies in medium using the SE-ADM system at an electron beam-acceleration of 6 kV, 5,000× magnification and −32 V bias. (b) An image of the streptavidin-conjugated 100-nm beads binding cells without anti-CD44 antibodies using SE-ADM system at an electron beam-acceleration of 10 kV and 3,000× magnification. (c) An image of unstained cancer cells at electron beam-acceleration of 8 kV and 5,000× magnification. (d–f) Expanded images of the red boxes in (a–c) with 20,000× magnification. In (d), many clear black spherical particles are dispersed over the whole area. In (e), few spherical beads are observed. In (f), almost no spherical beads are observed. (g) The average number of nano-beads/field with or without anti-CD44 antibody to the 4T1E/M3 cells. The average number of nano-beads/field is 29.5 with antibodies, 3.75 without antibodies and 1.25 in the control, in four scanned images of each condition at 20,000× magnification (an image size of 5.8 μm × 4.8 μm). Values are means ± SD; ***p < 0.0001. The scale bars represent 1 μm in (a–c), 500 nm in (d–f).