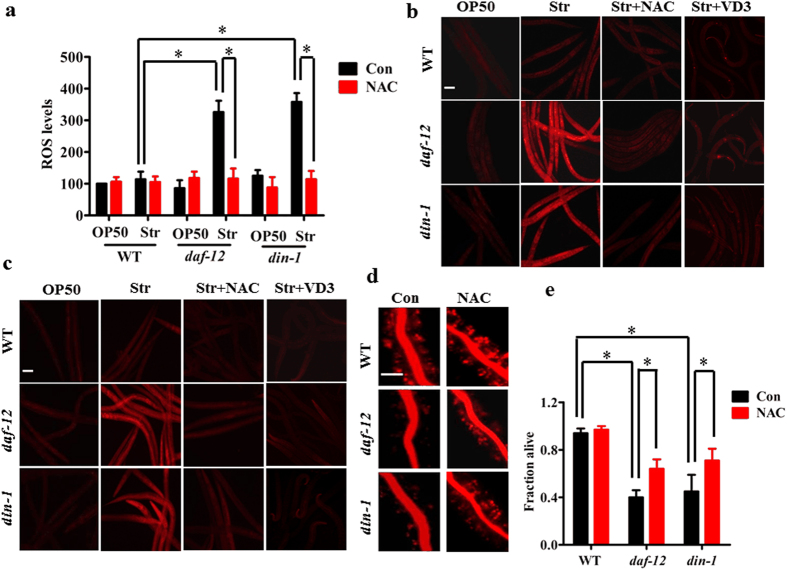
Figure 5. ROS formation is involved in worm death in daf-12(rh61rh411) or din-1(dh127) worms after starvation.
(a–c) Mutations in daf-12(rh61rh411) or din-1(dh127) resulted in an increase in ROS formation after 24 h of starvation. The levels of ROS were detected by DCF (a), DHE (b), and CellROX® Deep Red (c). The antioxidant NAC (1 mM) and vitamin D3 (0.5 mM) markedly diminished the increased ROS levels in starved daf-12(rh61rh411) or din-1(dh127) mutants. Scale bar, 100 μm. (d) NAC significantly suppressed necrosis in the daf-12(rh61rh411) or din-1(dh127) mutants after starvation. Fluorescence microscopy of acridine orange (AO)-labeled intestine of worms after two days of starvation. Scale bar, 50 μm. (e) NAC markedly promoted the survival of daf-12(rh61rh411) or din-1(dh127) mutants after five days of starvation. Results are means ± SD of three experiments. *P < 0.05. Str, starvation. Con, control.