Fig. 6.—
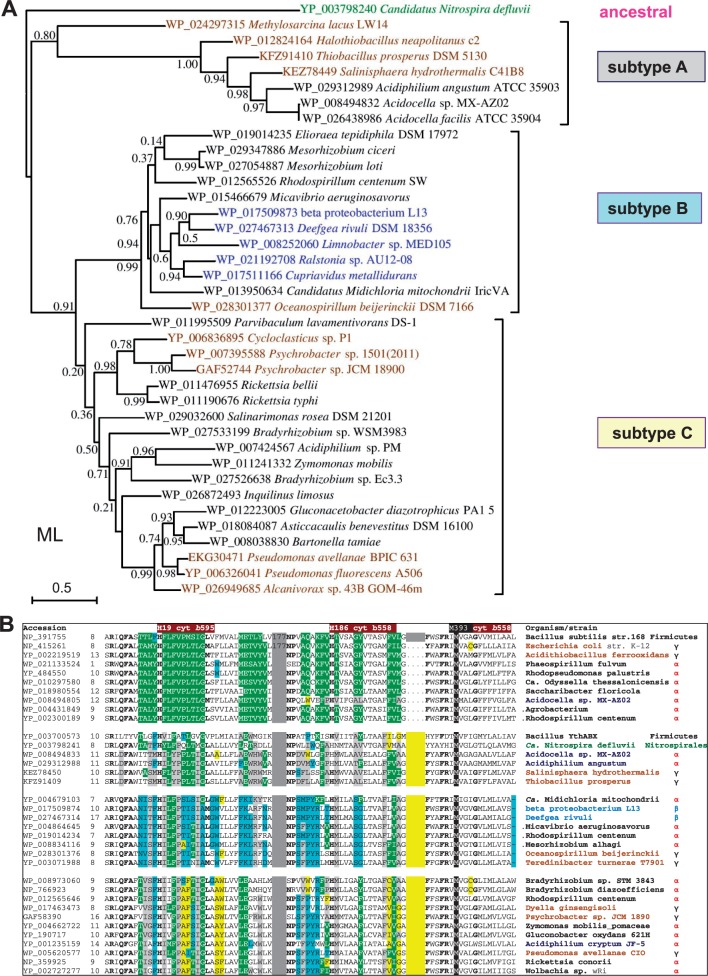
(A) Phylogenetic tree of representative cydB proteins of CIO type oxidases. The ML phylogenetic of tree cydB proteins (subunit II of bd oxidase) was built as in figure 4 A using as a guide the NJ tree obtained with a wide DELTABLAST search using as a query the 340 residues long cydB protein (subunit II) of Ca. Nitrospira defluvii (accession: YP_003798240) over a selection of taxa representing major groups of CIO oxidases, with the exception of δ-and Enterobacteria (see text). The tree was built on an improved alignment of the selected sequences (shown with their specific accession on the diagram as in fig. 4A) that was obtained using Gblocks (Talavera and Castresana 2007). The horizontal bar on the left indicates the fraction of amino acid changes estimated per site for a unit of branch length, whereas SH-like local support values are shown adjacent to nodes. Note the nearly complete match in topology with the tree obtained for the cydA protein (fig. 4A). However, topology differences with respect to the cydA tree of the same taxa (cf. fig. 4) are seen within the clade of subtype C, in particular for the position of the Bradyrhizobium, Inquilinus, and Zymomonas proteins. The relatively low SH-like local support values refer to the selection of 39 taxa used to build the tree shown; much stronger values were found for the same nodes by using wider selections of taxa (cf. supplementary fig. S1, Supplementary Material online). (B) Structural differences in cydA proteins correlate with the new classification of bd oxidases. Selected sequences of cydA proteins from all (sub)types of bd oxidases were first aligned with the program COBALT after a wide DELTABLAST search (cf. fig. 1); the alignment was then manually refined in the regions of poor sequence identity, removing gaps in the predicted transmembrane segments (cf. Degli Esposti et al. 1993). The alignment blocks containing the invariant hem ligands of bd oxidases (Mogi 2009; Borisov et al. 2011) were then extracted and compacted together, separated by narrow gray gaps and a yellow gap corresponding to the Q loop extension. Residue changes that are specific for each subtype of bd oxidases are highlighted as gray for CIO subtype A; pale blue for CIO subtype B; and yellow for CIO subtype C.