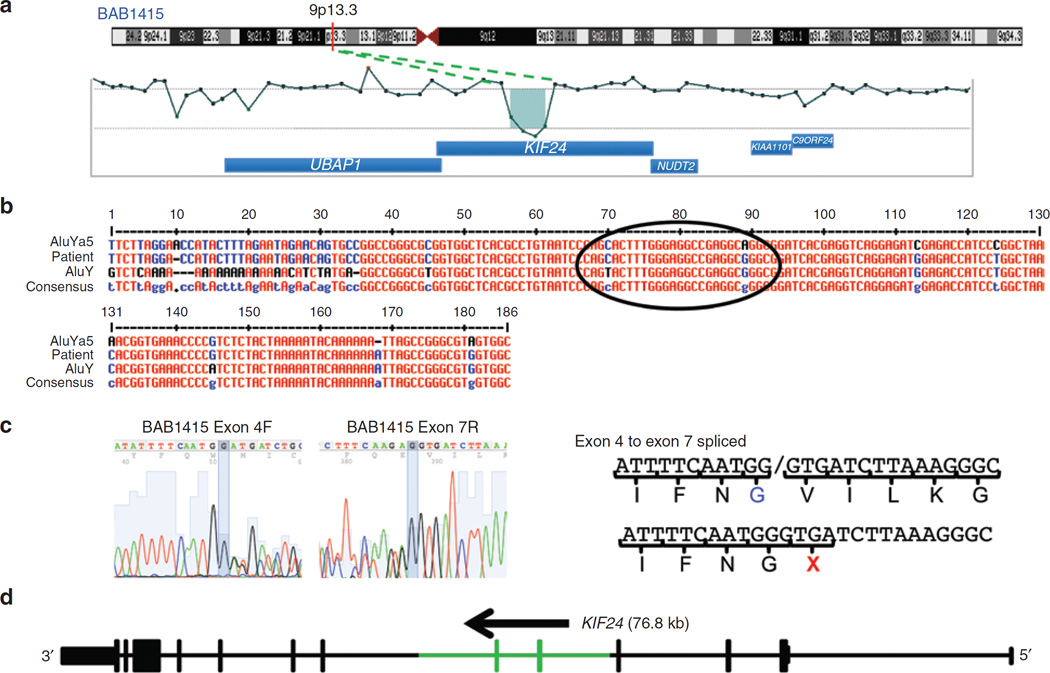
Figure 4. Array comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) and breakpoint junction studies of the KIF24 gene deletion in BAB1415.
(a) Chromosome 9 ideogram with G bands indicated (top). The location of KIF24 is shown with a red vertical line at 9p13.3. Array CGH results of the ~16.5-kb deletion involving exons 5 and 6 of KIF24. (b) Breakpoint sequence for KIF24 deletion using the MultAlin alignment tool. Proximal and distal reference sequences are mapped within AluYa5 and AluY sequences, respectively. The patient’s breakpoint sequence that matches the reference sequence is shown in blue, the mismatched sequence is shown in black, and perfect matching between all three sequences is depicted in red. The breakpoint junction is specified with a black circle where the transition occurred from the proximal to the distal reference sequence. (c) Skipping of exons 5 and 6 because of the deletion is confirmed in the complementary DNA. Peaks on peaks at the end of exon 4 and the beginning of exon 7 show the two species of RNA in BAB1415, both wild-type and deletion-containing. The lack of exons 5 and 6 in the deletion-containing RNA lead to a premature termination codon at the beginning of exon 7. (d) Graphic view of 13 exons of KIF24 (vertical bars, deleted exons 5 and 6 are shown in green); the size and orientation of the gene are shown above the exons.