Figure 1. A chemical compound binding to plasma membrane exhibits toxicity on AML cells.
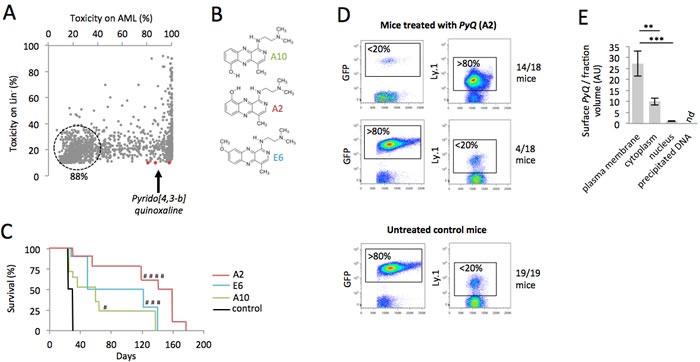
A. Scatter plot showing the toxicity of more than 7,400 indole chemical compounds (10ng/mL) after 18 hours of in vitro culture on HOXA9-MEIS1 and Lin−cells. B. Chemical structures of the PyQ compounds A2, E6 and A10. C. Kaplan-Meier survival curves of HOXA9-MEIS1 mice treated with A2, E6 or A10 (3mg/Kg), compared with control groups. Control; n = 19 mice, A10; n = 17 mice, E6; n = 10 mice, A2; n = 18 mice from two different donors. D. Quantification by flow cytometry of the leukemic cells (GFP+) and hematopoietic cells (Ly.1) in peripheral blood, 21 days after the transplantation. Mice were treated with compound A2; n = 18. Untreated control mice; n = 19. E. Localization of PyQ (A2) by HPLC chromatography in different subcellular compartments of THP1 cells showing important binding of PyQ to plasma membrane, n = 3 biological samples. Mean ± SEM. nd, not detected, **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; measured by Student's unpaired t test. #, P < 0.1; ###, P < 0.001; ####, P < 0.0001; measured by the Mantel Haenszel logrank test, compared with control group.
