Figure 4. Cell-permeable iron inhibits VEGF-A induced endothelial migration.
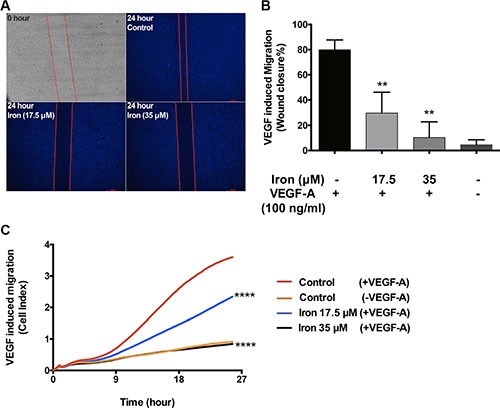
(A) Scratch wound assays were carried out to determine the effect of iron on VEGF-A (100 ng/ml) induced migration in HUVEC-I. Representative zero hour (immediately after the scratch) and twenty-four hour images of the scratch in the presence of iron (17.5 μM, 35 μM) are shown (2.5× magnification). (B) The histogram represents migration as percent closure of the wound area 24-hours after scratch wound. Data represent mean ± SD of three independent experiments. **P < 0.01. (C) Represents real-time migration of HUVEC-I towards a gradient of VEGF-A (100 ng/ml) in the presence of cell-permeable iron (17.5 μM, 35 μM). Electrical impedance (Cell index) was determined in real-time using CIM plates in an xCELLigence system. Data points are a mean of quadruplicate cultures. Statistical significance was determined from mean ± SD. Significant inhibition was seen as early as nine hours after treatment with cell-permeable iron. ****P < 0.0001.
