Figure 1. Ikaros and Foxp1 proteins interact in vivo.
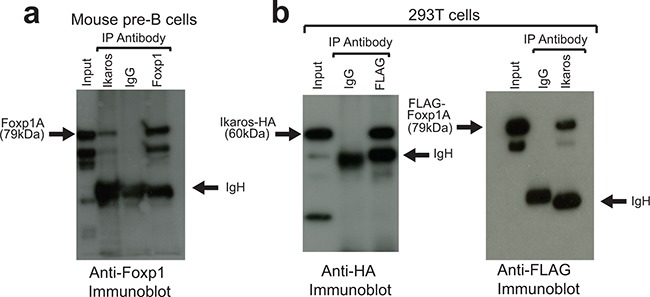
A. Protein extracts from murine fetal liver pre-B-cells were subjected to IP with anti-Foxp1 and anti-Ikaros antibodies and with control Ig and immunoblotted with anti-Foxp1. Arrows indicate full-length Foxp1 (Foxp1A) and IgH. The higher mobility bands are likely to be shorter Foxp1 splicing isoforms that are precipitated by the anti-Ikaros and anti-Foxp1 antibodies. B. IPs were carried out on protein lysates from 293T cells following co-transfection with FLAG-tagged Foxp1 and HA-tagged Ikaros constructs. Left panel: IP with anti-FLAG (Foxp1); immunoblotting with anti-HA (Ikaros). Right panel: IP with anti-Ikaros; immunoblotting with anti-FLAG (Foxp1). IP was carried out with anti-Ikaros antibody because the tagged Ikaros was only weakly precipitated from extracts by anti-HA, most likely due to epitope occlusion. Input for (A) and (B) = 5% of amount of protein lysate used for IPs.
