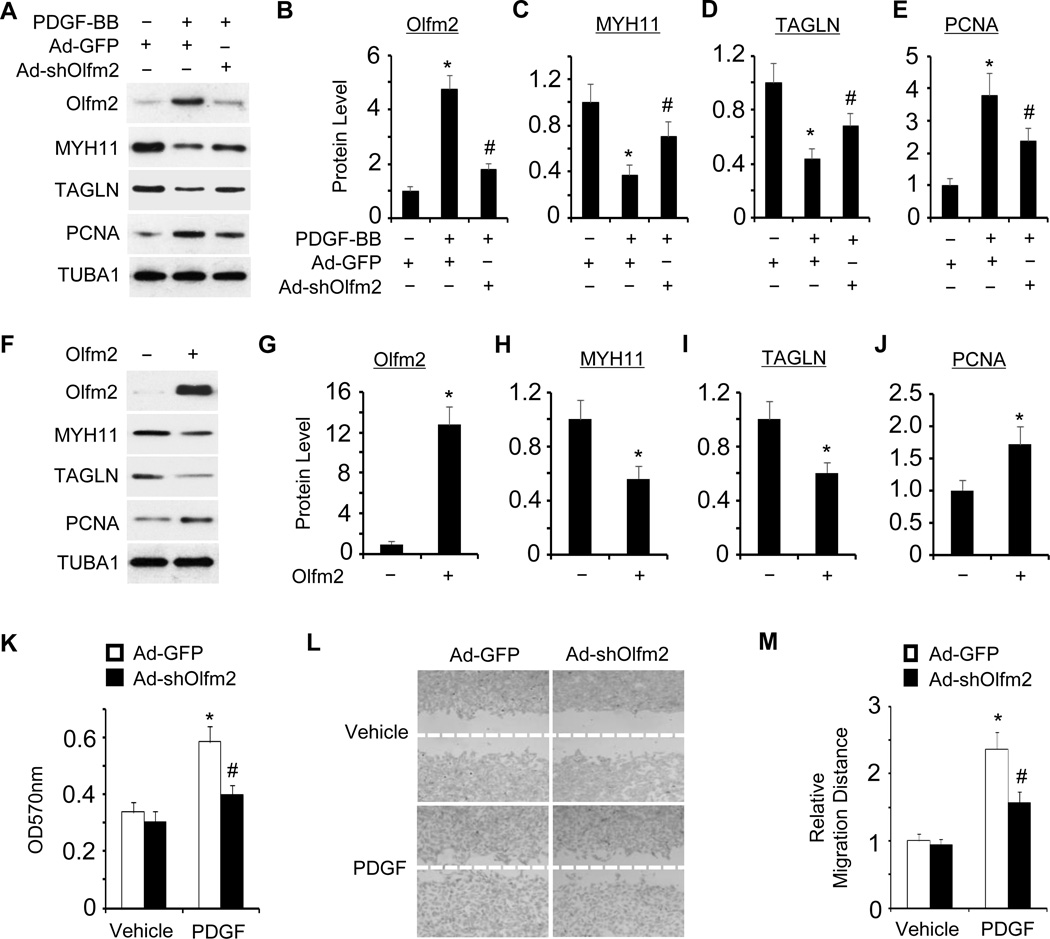
Figure 2. Olfm2 was essential for PDGF-BB-induced SMC phenotypic modulation.
A, Olfm2 knockdown reversed the effect of PDGF-BB on SMC marker and PCNA expression. RASMCs were transduced with Ad-GFP or Ad-shOlfm2 followed by vehicle (−) or PDGF-BB (+, 20 ng/ml) treatment for 24 h. Western blotting was performed to detect the expression of proteins as indicated. B–E, Quantification of the protein expression shown in A by normalizing to the TUBA1 level. *, P < 0.01 vs. Ad-GFP group with vehicle treatment (n=3). #, P < 0.01 vs. Ad-GFP group with PDGF-BB treatment (n=3). F, Forced Olfm2 expression promoted SMC phenotypic modulation. RASMCs were transfected with control or Olfm2 expression plasmid. Cell lysates were collected for Western blotting of the proteins indicated. G–J, Quantification of the protein expression shown in F by normalizing to the TUBA1 level. *, P < 0.01 vs. control group (n=3). K, Olfm2 knockdown diminished PDGF-BB-induced SMC proliferation. Ad-GFP- or Ad-shOlfm2-transduced RASMCs were seeded on 96-well plates and incubated with vehicle or PDGF-BB for 24 h. MTT assay was performed. *, P < 0.01 vs. Ad-GFP group with vehicle treatment. #, P < 0.01 vs. Ad-GFP group with PDGF-BB treatment (n=6). OD refers to the optical density normalized to the blank (medium only). L, Olfm2 knockdown diminished PDGF-BB-induced SMC migration. Ad-GFP- or Ad-shOlfm2-transduced RASMCs were seeded on 24-well plates containing a wound healing insert followed by incubation with vehicle or PDGF-BB for 24 h. Wound-healing assay was performed. M, Quantification of the relative migration distance shown in L. *, P < 0.01 vs. Ad-GFP group with vehicle treatment. #, P < 0.01 vs. Ad-GFP group with PDGF-BB treatment (n=3).