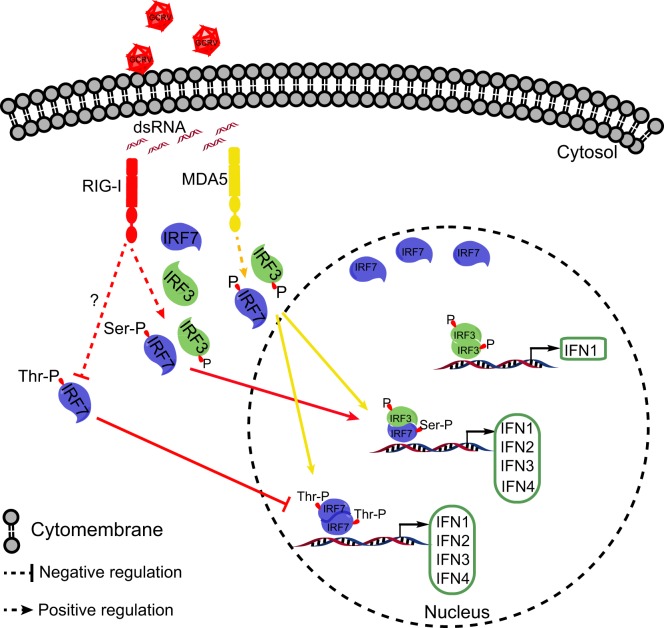
Figure 10.
Schematic representation of the difference between Ctenopharyngodon idella melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (CiMDA5) and C. idella retinoic acid-inducible gene I (CiRIG-I) in inducing grass carp IFNs (CiIFN) genes. The red arrows indicate the RIG-I pathway, while yellow arrows indicate the MDA5 pathway. Under grass carp reovirus (GCRV) infection, CiMDA5 and CiRIG-I facilitate the holistic phosphorylation levels of grass carp IFN regulatory factor 3 (CiIRF3) and CiIRF7. Both CiMDA5 and CiRIG-I enhance heterodimerization of CiIRF3 and CiIRF7. Differently, CiMDA5 facilitates but CiRIG-I weakens the threonine phosphorylation level of CiIRF7, which results in the status that CiMDA5 facilitates but CiRIG-I weakens the homodimerization of CiIRF7. This mechanism explains that CiMDA5 induces a stronger CiIFN-I response than CiRIG-I under GCRV infection in Ctenopharyngodon idella kidney cells.