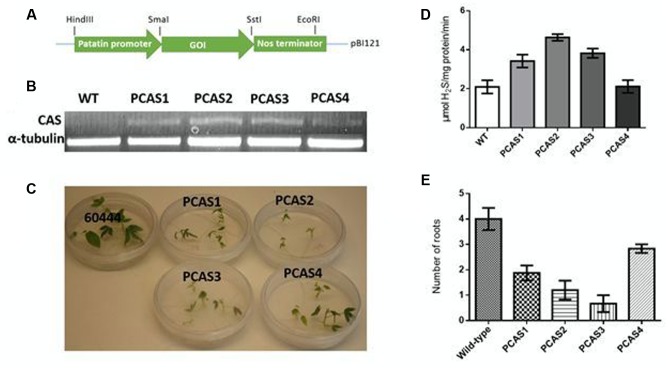
FIGURE 3.
(A) Gene cassette used in transforming cassava with β-cyanoalanine synthase (CAS) and nitrilase genes. The construct was assembled in a modified pBI121 plasmid where the gene of interest (GOI) was driven by a class I patatin promoter for root-specific expression. (B) CAS transcripts in wild-type (WT) and transgenic (PCAS1-4) cassava lines as detected by RT-PCR. RNA was extracted from 100 mg of 5 week-old in vitro cassava roots. RT-PCR was performed using primers for the CAS insert with tubulin as the internal control. (C) In vitro growth comparison of transgenic CAS-overexpressing plants (PCAS1-4) and wild-type (TMS 60444) plants after 3 weeks. (D) Expression of CAS increased the activity of the enzyme in cassava roots. The activity of CAS was correlated to reduced growth and root development (C,E). (E) Root development in in vitro transgenic CAS plants grown in MS medium for 3 weeks. Data are averages of n = 20. Statistical analysis was done by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s Multiple Comparison Test. All transgenics were significantly different from wild-type at P ≤ 0.05.