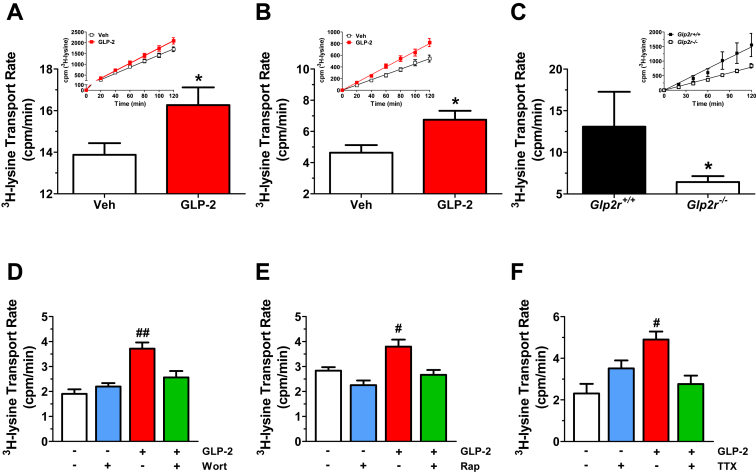
Figure 5.
GLP-2 stimulates lysine transport in murine small intestine independently of blood flow but requires PI3K-AKT/mTORC1 signaling and enteric neuronal activity. (A) C57BL/6J mice were treated acutely in vivo with either vehicle or GLP-2 (100 μg/kg) 30 min prior to tissue collection. 3H-Lysine transport was measured in full thickness jejunal tissue preparations mounted into Ussing chambers as described in Section 2. Data are mean ± SEM, n = 6–8 independent experiments performed in triplicate. *p < 0.05 GLP-2 vs. vehicle. (B) Seromuscular-stripped jejunal sections from C57BL/6J mice were mounted into Ussing chambers to measure 3H-Lysine transport rate following serosal addition of vehicle or GLP-2 (200 nM). Data are mean ± SEM, n = 7 independent experiments performed in triplicate. *p < 0.05 GLP-2 vs. vehicle. (C) 3H-Lysine transport using full thickness jejunal sections from Glp2r−/− mice and Glp2r+/+ littermate controls. Data are mean ± SEM, n = 4–6 independent experiments performed in triplicate. *p < 0.05 Glp2r+/+vs. Glp2r−/− mice. For (A–C), insets illustrate representative time-courses of 3H-Lysine appearance in the serosal chamber which were used to determine transport rate. Transport rate is operationally defined by the slope of the corresponding time course. (D–F) The rate of lysine transport was first assessed in seromuscular-stripped jejunal sections from C57BL/6J mice following the addition of vehicle or GLP-2 (200 nM) to the serosal compartment. 40 min later, either vehicle or (D) Wortmannin (Wort, 10−7 M), (E) Rapamycin (Rap, 10−7 M), or (F) tetrodotoxin (TTX, 2 μM) was added to the same compartment and lysine transport was re-assessed from 40 to 90 min. Basal and GLP-2-stimulated lysine transport was measured from 0 to 40 min, whereas transport in the presence of the indicated inhibitors was measured from 40 to 90 min #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 GLP-2 vs. vehicle, or Inhibitor vs. GLP-2 + Inhibitor. Data are mean ± SEM, n = 5–6 (D), n = 7–9 (E), or n = 3–6 (F) independent experiments performed in triplicate.