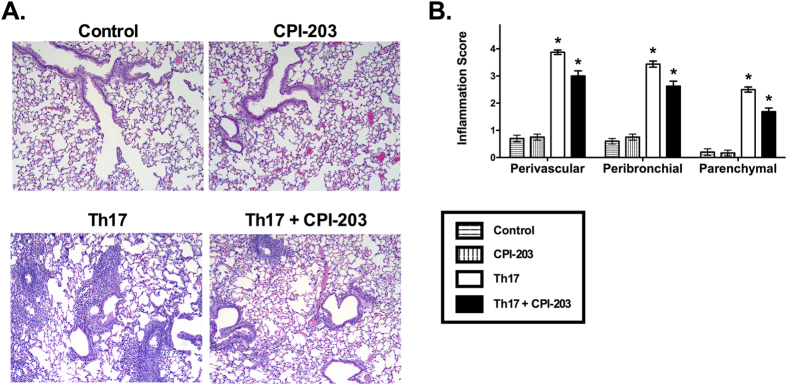
Figure 2. Inhibition of BET protein and chromatin interactions alters tissue-associated inflammation in the lungs of mice with Th17-induced allergic airway disease.
(A) Representative images of hematoxylin and eosin-stained lung sections (100x magnification) from OVA-treated BALB/c SCID mice that received Th17 cells (Th17 group) or PBS (control group) with and without CPI-203 treatment. (B) Perivascular, peribronchial, and parenchymal-associated inflammation in the entire lung section were quantified by an observer blinded to the identity of the samples. Graph shows data for control (n = 5), CPI-203 (n = 6), Th17 (n = 8), Th17+ CPI-203 (n = 8) combined from three independent experiments. *p < 0.05 when compared to all other groups, †p < 0.05 when compared to the CPI-203 group.