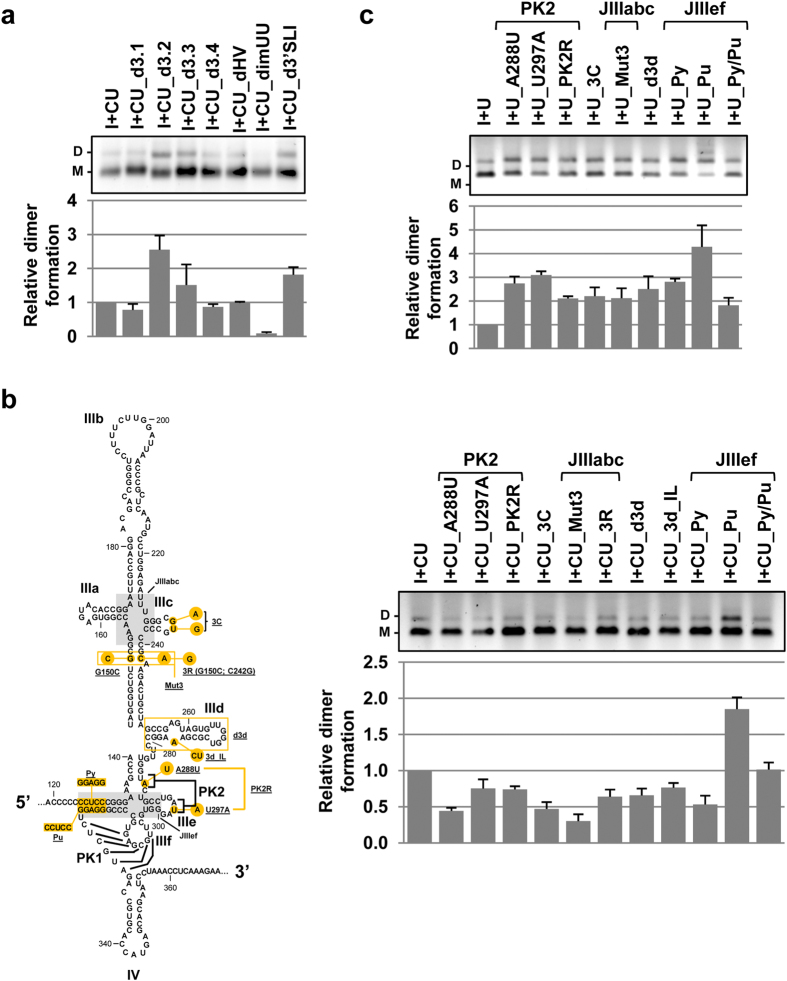
Figure 6. The IRES and the CRE control HCV dimerization efficiency.
Data obtained from HMX assays were used to design a series of variants bearing different deletions or single-point mutations within the CRE and IRES. (a) Dimerization efficiency was monitored for deletion mutants of different RNA domains located throughout the CRE and the 3′UTR for I+CU. A defective dimerization mutant, the so-called_dimUU molecule32 containing the point A9539U mutation in the DLS motif, was employed as a negative control. Dimeric and monomeric conformers were resolved by native agarose gel electrophoresis. The relative dimerization yield for each molecule tested was quantified and normalized to that obtained for the non-mutated control transcript. Data are the mean of at least three independent experiments ± standard deviation. (b,c) Single-point mutations were introduced in the IRES region as indicated, for both I+CU (b) and I+U (c). The effect on dimer formation was evaluated and quantified as noted above. Values represent the mean of three independent assays ± standard deviation.